MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment
- PMID: 15661851
- PMCID: PMC548345
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki198
MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment
Abstract
The accuracy of multiple sequence alignment program MAFFT has been improved. The new version (5.3) of MAFFT offers new iterative refinement options, H-INS-i, F-INS-i and G-INS-i, in which pairwise alignment information are incorporated into objective function. These new options of MAFFT showed higher accuracy than currently available methods including TCoffee version 2 and CLUSTAL W in benchmark tests consisting of alignments of >50 sequences. Like the previously available options, the new options of MAFFT can handle hundreds of sequences on a standard desktop computer. We also examined the effect of the number of homologues included in an alignment. For a multiple alignment consisting of approximately 8 sequences with low similarity, the accuracy was improved (2-10 percentage points) when the sequences were aligned together with dozens of their close homologues (E-value < 10(-5)-10(-20)) collected from a database. Such improvement was generally observed for most methods, but remarkably large for the new options of MAFFT proposed here. Thus, we made a Ruby script, mafftE.rb, which aligns the input sequences together with their close homologues collected from SwissProt using NCBI-BLAST.
Figures
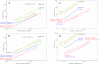
TCoffee, default;
PROBCONS, default;
CLUSTAL W, default;
MUSCLE-i,
muscle -maxiters 16;MUSCLE-2,
muscle -maxiters 1;MUSCLE-fast,
muscle -sv -maxiters 1 -diags1 -distance1 kbit20_3.
References
-
- Grasso C., Lee C. Combining partial order alignment and progressive multiple sequence alignment increases alignment speed and scalability to very large alignment problems. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1546–1556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

