A robust two-way semi-linear model for normalization of cDNA microarray data
- PMID: 15663789
- PMCID: PMC549200
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-14
A robust two-way semi-linear model for normalization of cDNA microarray data
Abstract
Background: Normalization is a basic step in microarray data analysis. A proper normalization procedure ensures that the intensity ratios provide meaningful measures of relative expression values.
Methods: We propose a robust semiparametric method in a two-way semi-linear model (TW-SLM) for normalization of cDNA microarray data. This method does not make the usual assumptions underlying some of the existing methods. For example, it does not assume that: (i) the percentage of differentially expressed genes is small; or (ii) the numbers of up- and down-regulated genes are about the same, as required in the LOWESS normalization method. We conduct simulation studies to evaluate the proposed method and use a real data set from a specially designed microarray experiment to compare the performance of the proposed method with that of the LOWESS normalization approach.
Results: The simulation results show that the proposed method performs better than the LOWESS normalization method in terms of mean square errors for estimated gene effects. The results of analysis of the real data set also show that the proposed method yields more consistent results between the direct and the indirect comparisons and also can detect more differentially expressed genes than the LOWESS method.
Conclusions: Our simulation studies and the real data example indicate that the proposed robust TW-SLM method works at least as well as the LOWESS method and works better when the underlying assumptions for the LOWESS method are not satisfied. Therefore, it is a powerful alternative to the existing normalization methods.
Figures

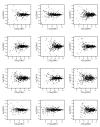
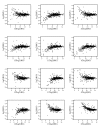
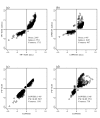
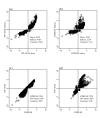
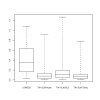
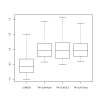
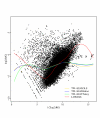
Similar articles
-
Use of normalization methods for analysis of microarrays containing a high degree of gene effects.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Nov 28;9:505. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-505. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 19040742 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological study of affine transformations of gene expression data with proposed robust non-parametric multi-dimensional normalization method.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Mar 1;7:100. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-100. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16509971 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized LOWESS normalization parameter selection for DNA microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Dec 9;5:194. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-194. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15588297 Free PMC article.
-
Normalization of microarray data: single-labeled and dual-labeled arrays.Mol Cells. 2006 Dec 31;22(3):254-61. Mol Cells. 2006. PMID: 17202852 Review.
-
Microarray data analysis: from disarray to consolidation and consensus.Nat Rev Genet. 2006 Jan;7(1):55-65. doi: 10.1038/nrg1749. Nat Rev Genet. 2006. PMID: 16369572 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of normalization methods for analysis of microarrays containing a high degree of gene effects.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Nov 28;9:505. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-505. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 19040742 Free PMC article.
-
Using generalized procrustes analysis (GPA) for normalization of cDNA microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Jan 16;9:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-25. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18199333 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating different methods of microarray data normalization.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Oct 23;7:469. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-469. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17059609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Hedge P, Qi R, Abernathy K, Gay C, Dharap S, Gaspard R, Earle-Hughes J, Snesrud E, Lee N, Quackenbush J. A concise guide to cDNA microarray analysis. Biotechniques. 2000;29:548–562. - PubMed
-
- Yang YH, Dudoit S, Luu P, Speed TP. Normalization for cDNA microarray. Microarrays: Optical Technologies and Informatics SPIE, Society for Optical Engineering, San Jose, CA. 2001;4266
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

