Origin of the amphibian chytrid fungus
- PMID: 15663845
- PMCID: PMC3323396
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1012.030804
Origin of the amphibian chytrid fungus
Abstract
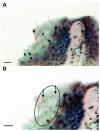
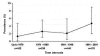
The sudden appearance of chytridiomycosis, the cause of amphibian deaths and population declines in several continents, suggests that its etiologic agent, the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, was introduced into the affected regions. However, the origin of this virulent pathogen is unknown. A survey was conducted of 697 archived specimens of 3 species of Xenopus collected from 1879 to 1999 in southern Africa in which the histologic features of the interdigital webbing were analyzed. The earliest case of chytridiomycosis found was in a Xenopus laevis frog in 1938, and overall prevalence was 2.7%. The prevalence showed no significant differences between species, regions, season, or time period. Chytridiomycosis was a stable endemic infection in southern Africa for 23 years before any positive specimen was found outside Africa. We propose that Africa is the origin of the amphibian chytrid and that the international trade in X. laevis that began in the mid-1930s was the means of dissemination.
Figures
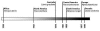
References
-
- Speare R; Core Working Group of Getting the Jump on Amphibian Disease. Nomination for listing of amphibian chytridiomycosis as a key threatening process under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. In: Speare R, Steering Committee of Getting the Jump on Amphibian Disease, editors. Developing management strategies to control amphibian diseases: decreasing the risks due to communicable diseases. Townsville, Australia: School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, James Cook University; 2001. p. 163–84. Available from http://www.jcu.edu.au/school/phtm/PHTM/frogs/adms/attach7.pdf
-
- Lips KR. Mass mortality of the anuran fauna at an upland site in Panama. Conserv Biol. 1999;13:11725. 10.1046/j.1523-1739.1999.97185.x - DOI
-
- Bonaccorso E, Guayasamin JM, Méndez D, Speare R. Chytridiomycosis in a Venezuelan amphibian (Bufonidae: Atelopus cruciger). Herpetol Rev. 2003;34:331–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
