Animal-to-human transmission of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104A variant
- PMID: 15663868
- PMCID: PMC3323380
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1012.040286
Animal-to-human transmission of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104A variant
Abstract
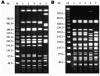
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium was isolated from a pig, a calf, and a child on a farm in the Netherlands. The isolates were indistinguishable by phenotyping and genotyping methods, which suggests nonfoodborne animal-to-animal and animal-to-human transmission. Persons in close contact with farm animals should be aware of this risk.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salmonella transmission through splash exposure during a bovine necropsy.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2007 Fall;4(3):387-90. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2007.0021. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2007. PMID: 17883322
-
[Report on Salmonella isolates in livestock, food and feed, received at the German national reference laboratory for Salmonella during 2004-2008].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2010 Jul-Aug;123(7-8):265-77. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2010. PMID: 20690538 German.
-
Salmonella Typhimurium persistence in a Hunter Valley dairy herd.Aust Vet J. 2007 Nov;85(11):446-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.2007.00224.x. Aust Vet J. 2007. PMID: 17970848
-
Salmonella typhimurium DT104: a virulent and drug-resistant pathogen.Can Vet J. 1998 Sep;39(9):559-65. Can Vet J. 1998. PMID: 9752592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium in four animal facilities.Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Aug;11(8):1235-41. doi: 10.3201/eid1108.050111. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16102313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hsp100 Molecular Chaperone ClpB and Its Role in Virulence of Bacterial Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 18;22(10):5319. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105319. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Molecular Detection of Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi, Enteritidis, Infantis, and Typhimurium.Iran J Public Health. 2017 Jan;46(1):103-111. Iran J Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28451535 Free PMC article.
-
Global Genomic Epidemiology of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium DT104.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Apr 4;82(8):2516-26. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03821-15. Print 2016 Apr. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26944846 Free PMC article.
-
Public farms: hygiene and zoonotic agents.Epidemiol Infect. 2007 Oct;135(7):1174-83. doi: 10.1017/S0950268807008072. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Epidemiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17313696 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing Frequencies of Antibiotic Resistant Non-typhoidal Salmonella Infections in Michigan and Risk Factors for Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Nov 8;6:250. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00250. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31781566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van den Brandhof WE, van Pelt W, Wagenaar JA, van Duynhoven YTHP. Study on the sources of human campylobacteriosis and salmonellosis in the Netherlands. Infectieziekten Bulletin. 2003;14:132–5.
-
- Wall PG, Morgan D, Lamden K, Ryan M, Griffin M, Threlfall EJ, et al. A case control study of infection with an epidemic strain of multiresistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT 104 in England and Wales. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1994;4:R130–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
