Animal-to-human transmission of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104A variant
- PMID: 15663868
- PMCID: PMC3323380
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1012.040286
Animal-to-human transmission of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104A variant
Abstract
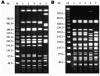
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium was isolated from a pig, a calf, and a child on a farm in the Netherlands. The isolates were indistinguishable by phenotyping and genotyping methods, which suggests nonfoodborne animal-to-animal and animal-to-human transmission. Persons in close contact with farm animals should be aware of this risk.
Figures
References
-
- Van den Brandhof WE, van Pelt W, Wagenaar JA, van Duynhoven YTHP. Study on the sources of human campylobacteriosis and salmonellosis in the Netherlands. Infectieziekten Bulletin. 2003;14:132–5.
-
- Wall PG, Morgan D, Lamden K, Ryan M, Griffin M, Threlfall EJ, et al. A case control study of infection with an epidemic strain of multiresistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT 104 in England and Wales. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1994;4:R130–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
