Bacterial glycolipids and analogs as antigens for CD1d-restricted NKT cells
- PMID: 15665086
- PMCID: PMC547854
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408696102
Bacterial glycolipids and analogs as antigens for CD1d-restricted NKT cells
Abstract
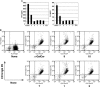
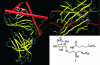
The CD1 family of proteins binds self and foreign glycolipids for presentation to CD1-restricted T cells. To identify previously uncharacterized active CD1 ligands, especially those of microbial origin, numerous glycolipids were synthesized and tested for their ability to stimulate mouse and human natural killer T (NKT) cells. They included analogs of the well known NKT cell agonist alpha-galactosyl ceramide (alpha-GalCer), bacterial glycolipids, and variations of the self-glycolipid, sulfatide. Bacterial glycolipids, alpha-galacturonosyl-ceramides from Sphingomonas wittichii, although structurally similar to alpha-GalCer, have significant differences in the sugar head group as well as the ceramide portion. The Sphingomonas glycosphingolipids (GSLs) and sulfatide variants were shown to activate human NKT cells as measured by IL-4 and IFN-gamma secretion. Moreover, CD1d-dimer staining revealed human NKT cell reactivity toward these GSLs and to the sulfatides in a fashion comparable with alpha-GalCer. Because alpha-GalCer is a marine-sponge-derived ligand, our study here shows that bacterium-derived antigens are also able to stimulate mouse and human NKT cells.
Figures
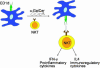
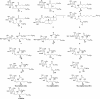
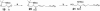
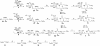
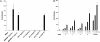
Similar articles
-
Recognition of bacterial glycosphingolipids by natural killer T cells.Nature. 2005 Mar 24;434(7032):520-5. doi: 10.1038/nature03407. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15791257
-
Natural killer T cells recognize diacylglycerol antigens from pathogenic bacteria.Nat Immunol. 2006 Sep;7(9):978-86. doi: 10.1038/ni1380. Epub 2006 Aug 20. Nat Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16921381
-
Cell wall glycosphingolipids of Sphingomonas paucimobilis are CD1d-specific ligands for NKT cells.Eur J Immunol. 2005 Jun;35(6):1692-701. doi: 10.1002/eji.200526157. Eur J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15915536
-
Glycolipids and phospholipids as natural CD1d-binding NKT cell ligands.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Aug;63(16):1889-98. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6073-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16794785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycolipids as immune modulatory tools.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006 Nov;6(11):1249-53. doi: 10.2174/138955706778742722. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 17100636 Review.
Cited by
-
The natural killer T lymphocyte: a player in the complex regulation of autoimmune diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Feb;143(2):194-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02942.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16412042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced immune response to Borrelia burgdorferi in the absence of γδ T cells.Infect Immun. 2011 Oct;79(10):3940-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00148-11. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21768278 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine Kinase Blockade Leads to Increased Natural Killer T Cell Responses to Mantle Cell Lymphoma.Cells. 2020 Apr 21;9(4):1030. doi: 10.3390/cells9041030. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326225 Free PMC article.
-
Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria.Nat Immunol. 2011 Sep 4;12(10):966-74. doi: 10.1038/ni.2096. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21892173 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal processing of sulfatide analogs alters target NKT cell specificity and immune responses in cancer.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 21;134(4):e165281. doi: 10.1172/JCI165281. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 38127463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Porcelli, S. A. & Modlin, R. L. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 297-329. - PubMed
-
- Joyce, S. & Kaer, L. V. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 95-104. - PubMed
-
- Calabi, F., Jarvis, J. M., Martin, L. & Milstein, C. (1989) Eur. J. Immunol. 19, 285-292. - PubMed
-
- Zeng, Z., Castano, A. R., Segelke, B. W., Stura, E. A., Peterson, P. A. & Wilson, I. A. (1997) Science 277, 339-345. - PubMed
-
- Zajonc, D. M., Elsliger, M. A., Teyton, L. & Wilson, I. A. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4, 808-815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

