Unparalleled complexity of the MHC class I region in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 15665097
- PMCID: PMC545086
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409084102
Unparalleled complexity of the MHC class I region in rhesus macaques
Abstract
The highly polymorphic gene products of the classical MHC class I genes in humans (HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C) play a critical role in the immune defense against intracellular infections. Because non-human primates are important models for AIDS vaccine research, rhesus monkeys from a thoroughly pedigreed and serotyped colony were subjected to full-length cDNA analysis of MHC class I gene transcripts. Rhesus macaques express multiple dominant Mamu-A and Mamu-B transcripts (majors) per chromosome, which are characterized by high expression levels. The presence of additional cDNAs with low levels of expression (minors) suggests evidence for transcriptional control of MHC class I genes. Moreover, phylogenetic analyses illustrate that most of the Mamu-A and Mamu-B loci/lineages identified display no or only limited levels of allelic polymorphism. Thus, MHC class I diversity in rhesus macaques is typified by the existence of an unmatched high number of Mamu-A and Mamu-B region configurations that exhibit polymorphism with regard to the number and combination of transcribed loci present per chromosome.
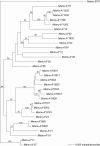
Figures



References
-
- Parham, P. & Ohta, T. (1996) Science 272, 67–74. - PubMed
-
- Vilches, C. & Parham, P. (2002) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 217–251. - PubMed
-
- Martin, M. P., Bashirova, A., Traherne, J., Trowsdale, J. & Carrington, M. (2003) J. Immunol. 172, 2192–2195. - PubMed
-
- Ishitani, A., Sageshima, N., Lee, N., Dorofeeva, N., Hatake, K., Marquardt, H. & Geraghty, D. E. (2003) J. Immunol. 171, 1376–1384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

