Role of actin DNase-I-binding loop in myosin subfragment 1-induced polymerization of G-actin: implications for the mechanism of polymerization
- PMID: 15665122
- PMCID: PMC1305383
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.049155
Role of actin DNase-I-binding loop in myosin subfragment 1-induced polymerization of G-actin: implications for the mechanism of polymerization
Abstract
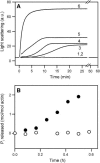
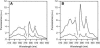
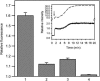
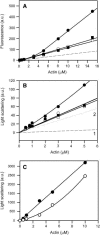
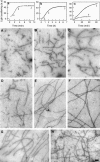
Proteolytic cleavage of actin between Gly(42) and Val(43) within its DNase-I-binding loop (D-loop) abolishes the ability of Ca-G-actin to spontaneously polymerize in the presence of KCl. Here we show that such modified actin is assembled into filaments, albeit at a lower rate than unmodified actin, by myosin subfragment 1 (S1) carrying the A1 essential light chain but not by S1(A2). S1 titration of pyrene-G-actin showed a diminished affinity of cleaved actin for S1, but this could be compensated for by using S1 in excess. The most significant effect of the cleavage, revealed by measuring the fluorescence of pyrene-actin and light-scattering intensities as a function of actin concentration at saturating concentrations of S1, is strong inhibition of association of G-actin-S1 complexes into oligomers. Measurements of the fluorescence of dansyl cadaverine attached to Gln(41) indicate substantial inhibition of the initial association of G-actin-S1 into longitudinal dimers. The data provide experimental evidence for the critical role of D-loop conformation in both longitudinal and lateral, cross-strand actin-actin contact formation in the nucleation reaction. Electron microscopic analysis of the changes in filament-length distribution during polymerization of actin by S1(A1) and S1(A2) suggests that the mechanism of S1-induced polymerization is not substantially different from the nucleation-elongation scheme of spontaneous actin polymerization.
Figures
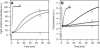

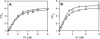


Similar articles
-
Interaction of myosin subfragment 1 with forms of monomeric actin.Biochemistry. 2003 Mar 18;42(10):3060-9. doi: 10.1021/bi020597q. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12627973
-
Interaction and polymerization of the G-actin-myosin head complex: effect of DNase I.Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):10005-14. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a016. Biochemistry. 1993. PMID: 8399127
-
Proteolytic cleavage of actin within the DNase-I-binding loop changes the conformation of F-actin and its sensitivity to myosin binding.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Mar 16;1478(1):138-51. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(00)00005-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10719182
-
Myosin subfragment-1-induced polymerization of G-actin. Formation of partially decorated filaments at high actin-S1 ratios.J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3829-37. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8106427
-
Cross-linked long-pitch actin dimer forms stoichiometric complexes with gelsolin segment 1 and/or deoxyribonuclease I that nonproductively interact with myosin subfragment 1.Biochemistry. 2008 Sep 2;47(35):9335-43. doi: 10.1021/bi800410z. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18693756
Cited by
-
Structural basis for tunable control of actin dynamics by myosin-15 in mechanosensory stereocilia.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul 22;8(29):eabl4733. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4733. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35857845 Free PMC article.
-
The Balance between Protealysin and Its Substrate, the Outer Membrane Protein OmpX, Regulates Serratia proteamaculans Invasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):6159. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116159. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Actin-Specific Endoproteases Grimelysin and Protealysin as Virulence Factors Contributing to the Invasive Activities of Serratia.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 4;21(11):4025. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114025. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32512842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac myosin-binding protein C decorates F-actin: implications for cardiac function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 25;105(47):18360-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808903105. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19011110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchoin, L., S. Fievez, F. Travers, M.-F. Carlier, and D. Pantaloni. 1995. Kinetics of the interaction of myosin subfragment-1 with G-actin. Effect of nucleotides and DNaseI. J. Biol. Chem. 270:7125–7133. - PubMed
-
- Carlier, M.-F. 1991. Actin: protein structure and filament dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 266:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Carlier, M.-F., and D. Pantaloni. 1997. Control of actin dynamics in cell motility. J. Mol. Biol. 269:459–467. - PubMed
-
- Carlier, M.-F., D. Pantaloni, and E. D. Korn. 1986. Fluorescence measurements of the binding of cations to high-affinity and low-affinity sites on ATP-G-actin. J. Biol. Chem. 261:10778–10784. - PubMed
-
- Chen, T., M. Heigentz, and E. Reisler. 1992. Myosin subfragment-1 and structural elements of G-actin: effects of S-1(A2) on sequences 39–52 and sequences 61–69 in subdomain-2 of G-actin. Biochemistry. 31:2941–2946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

