The effect of ADHD on the life of an individual, their family, and community from preschool to adult life
- PMID: 15665153
- PMCID: PMC1765272
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2004.059006
The effect of ADHD on the life of an individual, their family, and community from preschool to adult life
Abstract
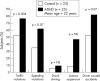
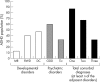
Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may affect all aspects of a child's life. Indeed, it impacts not only on the child, but also on parents and siblings, causing disturbances to family and marital functioning. The adverse effects of ADHD upon children and their families changes from the preschool years to primary school and adolescence, with varying aspects of the disorder being more prominent at different stages. ADHD may persist into adulthood causing disruptions to both professional and personal life. In addition, ADHD has been associated with increased healthcare costs for patients and their family members.
Figures

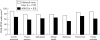
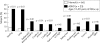

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
