Microarray analysis confirms the specificity of a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast RNA stability mutant
- PMID: 15665248
- PMCID: PMC1065354
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.053256
Microarray analysis confirms the specificity of a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast RNA stability mutant
Abstract
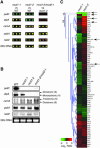
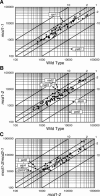
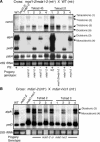
The expression of chloroplast and mitochondrial genes depends on nucleus-encoded proteins, some of which control processing, stability, and/or translation of organellar RNAs. To test the specificity of one such RNA stability factor, we used two known Chlamydomonas reinhardtii nonphotosynthetic mutants carrying mutations in the Mcd1 nuclear gene (mcd1-1 and mcd1-2). We previously reported that these mutants fail to accumulate the chloroplast petD mRNA and its product, subunit IV of the cytochrome b6/f complex, which is essential for photosynthesis. Such mutants are generally presumed to be gene specific but are not tested rigorously. Here, we have used microarray analysis to assess changes in chloroplast, mitochondrial, and nuclear RNAs, and since few other RNAs were significantly altered in these mutants, conclude that Mcd1 is indeed specifically required for petD mRNA accumulation. In addition, a new unlinked nuclear mutation was discovered in mcd1-2, which greatly reduced chloroplast atpA mRNA accumulation. Genetic analyses showed failure to complement mda1-ncc1, where atpA-containing transcripts are similarly affected (D. Drapier, J. Girard-Bascou, D.B. Stern, F.-A. Wollman [2002] Plant J 31: 687-697), and we have named this putative new allele mda1-2. We conclude that DNA microarrays are efficient and useful for characterizing the specificity of organellar RNA accumulation mutants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A spontaneous tRNA suppressor of a mutation in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii nuclear MCD1 gene required for stability of the chloroplast petD mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jun 9;33(10):3372-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki651. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15947135 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear suppressors define three factors that participate in both 5' and 3' end processing of mRNAs in Chlamydomonas chloroplasts.Plant J. 2006 May;46(3):448-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02711.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 16623905
-
A dominant nuclear mutation in Chlamydomonas identifies a factor controlling chloroplast mRNA stability by acting on the coding region of the atpA transcript.Plant J. 2002 Sep;31(6):687-97. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01387.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12220261
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of chloroplast gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant Mol Biol. 1996 Oct;32(1-2):327-41. doi: 10.1007/BF00039389. Plant Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8980486 Review.
-
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as the photosynthetic yeast.Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:209-30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.29.120195.001233. Annu Rev Genet. 1995. PMID: 8825474 Review.
Cited by
-
Cluster analysis and comparison of various chloroplast transcriptomes and genes in Arabidopsis thaliana.DNA Res. 2009 Feb;16(1):31-44. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsn031. Epub 2008 Dec 23. DNA Res. 2009. PMID: 19106172 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory sequences of orthologous petD chloroplast mRNAs are highly specific among Chlamydomonas species.Plant Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;60(3):405-22. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-4477-z. Plant Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16514563
-
Cryptochrome 2 extensively regulates transcription of the chloroplast genome in tomato.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Mar 1;7(4):456-471. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12082. eCollection 2017 Apr. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28396831 Free PMC article.
-
A tiling microarray for global analysis of chloroplast genome expression in cucumber and other plants.Plant Methods. 2011 Sep 28;7:29. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-7-29. Plant Methods. 2011. PMID: 21952044 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic microalgae genomics. The essence of being a plant.Plant Physiol. 2005 Feb;137(2):397-8. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.900136. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15710680 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baena-Gonzalez E, Allahverdiyeva Y, Svab Z, Maliga P, Josse EM, Kuntz M, Maenpaa P, Aro EM (2003) Deletion of the tobacco plastid psbA gene triggers an upregulation of the thylakoid-associated NAD(P)H dehydrogenase complex and the plastid terminal oxidase (PTOX). Plant J 35: 704–716 - PubMed
-
- Barkan A, Goldschmidt-Clermont M (2000) Participation of nuclear genes in chloroplast gene expression. Biochimie 82: 559–572 - PubMed
-
- Brazma A, Hingamp P, Quackenbush J, Sherlock G, Spellman P, Stoeckert C, Aach J, Ansorge W, Ball CA, Causton HC, et al (2001) Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)—toward standards for microarray data. Nat Genet 29: 365–371 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

