Targeting effector memory T cells with a selective peptide inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels for therapy of autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 15665253
- PMCID: PMC4275123
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.104.008193
Targeting effector memory T cells with a selective peptide inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels for therapy of autoimmune diseases
Abstract
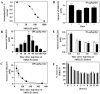
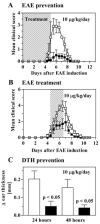
The voltage-gated Kv1.3 K(+) channel is a novel target for immunomodulation of autoreactive effector memory T (T(EM)) cells that play a major role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. We describe the characterization of the novel peptide ShK(L5) that contains l-phosphotyrosine linked via a nine-atom hydrophilic linker to the N terminus of the ShK peptide from the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus. ShK(L5) is a highly specific Kv1.3 blocker that exhibits 100-fold selectivity for Kv1.3 (K(d) = 69 pM) over Kv1.1 and greater than 250-fold selectivity over all other channels tested. ShK(L5) suppresses the proliferation of human and rat T(EM) cells and inhibits interleukin-2 production at picomolar concentrations. Naive and central memory human T cells are initially 60-fold less sensitive than T(EM) cells to ShK(L5) and then become resistant to the peptide during activation by up-regulating the calcium-activated K(Ca)3.1 channel. ShK(L5) does not exhibit in vitro cytotoxicity on mammalian cell lines and is negative in the Ames test. It is stable in plasma and when administered once daily by subcutaneous injection (10 mug/kg) attains "steady state" blood levels of approximately 300 pM. This regimen does not cause cardiac toxicity assessed by continuous EKG monitoring and does not alter clinical chemistry and hematological parameters after 2-week therapy. ShK(L5) prevents and treats experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and suppresses delayed type hypersensitivity in rats. ShK(L5) might prove useful for therapy of autoimmune disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Atwal KS, Vaccaro W, Lloyd J, Finlay H, Yan L, Bhandaru RS. inventors, Bristol-Myers Squibb, assignee. Heterocyclic dihydropyrimidines as potassium channel inhibitors. WO0140231. World patent. 2001 2001 Jun 7;
-
- Baell JB, Gable RW, Harvey AJ, Toovey N, Herzog T, Hansel W, Wulff H. Khellinone derivatives as blockers of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3: synthesis and immunosuppressive activity. J Med Chem. 2004;47:2326–2336. - PubMed
-
- Bagdány M, Batista CVF, Valdez-Cruz NA, Somodi S, Rodriguez de la Vega RC, Licea AF, Gáspár R, Possani LD, Panyi G. Anuroctoxin, a new scorpion toxin of the α-KTx 6 subfamily, is highly selective for Kv1.3 over IKCa1 ion channels of human T lymphocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;67:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Bao J, Miao S, Kayser F, Kotliar AJ, Baker RK, Doss GA, Felix JP, Bugianesi RM, Slaughter RS, Kaczorowski GJ. Potent Kv1.3 inhibitors from correolide-modification of the C18 position. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005;15:447–451. - PubMed
-
- Bardien-Kruger S, Wulff H, Arieff Z, Brink P, Chandy KG, Corfield V. Characterisation of the human voltage-gated potassium channel gene, KCNA7, a candidate gene for inherited cardiac disorders and its exclusion as cause of progressive familial heart block I (PFHBI) Eur J Hum Genet. 2002;10:36–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

