Erythromycin exerts in vivo anti-inflammatory activity downregulating cell adhesion molecule expression
- PMID: 15665859
- PMCID: PMC1575992
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706021
Erythromycin exerts in vivo anti-inflammatory activity downregulating cell adhesion molecule expression
Abstract
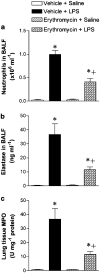
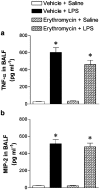
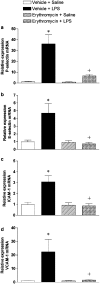
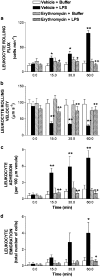
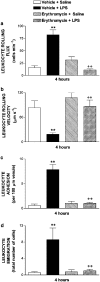
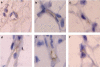
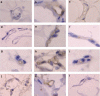
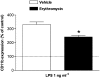
1. Macrolides have long been used as anti-bacterial agents; however, there is some evidence that may exert anti-inflammatory activity. Therefore, erythromycin was used to characterize the mechanisms involved in their in vivo anti-inflammatory activity. 2. Erythromycin pretreatment (30 mg kg(-1) day(-1) for 1 week) reduced the lipopolysaccharide (LPS; intratracheal, 0.4 mg kg(-1))-induced increase in neutrophil count and elastase activity in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissue myeloperoxidase activity, but failed to decrease tumor necrosis factor-alpha and macrophage-inflammatory protein-2 augmented levels in BALF. Erythromycin pretreatment also prevented lung P-selectin, E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) mRNA upregulation in response to airway challenge with LPS. 3. Mesentery superfusion with LPS (1 mug ml(-1)) induced a significant increase in leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions at 60 min. Erythromycin pretreatment abolished the increases in these parameters. 4. LPS exposure of the mesentery for 4 h caused a significant increase in leukocyte rolling flux, adhesion and emigration, which were inhibited by erythromycin by 100, 93 and 95%, respectively. 5. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that LPS exposure of the mesentery for 4 h caused a significant enhancement in P-selectin, E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression that was downregulated by erythromycin pretreatment. 6. Flow cytometry analysis indicated that erythromycin pretreatment inhibited LPS-induced CD11b augmented expression in rat neutrophils. 7. In conclusion, erythromycin inhibits leukocyte recruitment in the lung and this effect appears mediated through downregulation of CAM expression. Therefore, macrolides may be useful in the control of neutrophilic pulmonary diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rolipram inhibits leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions in vivo through P- and E-selectin downregulation.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;135(8):1872-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704644. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11959789 Free PMC article.
-
Erythromycin inhibits beta2-integrins (CD11b/CD18) expression, interleukin-8 release and intracellular oxidative metabolism in neutrophils.Respir Med. 2000 Jul;94(7):654-60. doi: 10.1053/rmed.1999.0781. Respir Med. 2000. PMID: 10926336
-
Budlein A from Viguiera robusta inhibits leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions, adhesion molecule expression and inflammatory mediators release.Phytomedicine. 2009 Oct;16(10):904-15. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.04.002. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Phytomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19524419
-
Inhibitory effects of flavonoids extracted from licorice on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute pulmonary inflammation in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Feb;9(2):194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2008.11.004. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19071231
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of neutrophil elastase inhibitors.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003 May;4(5):556-65. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12833649 Review.
Cited by
-
The immune response and antibacterial therapy.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Apr;204(2):151-9. doi: 10.1007/s00430-014-0355-0. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25189424 Review.
-
Effect of erythromycin on mortality and the host response in critically ill patients with sepsis: a target trial emulation.Crit Care. 2022 May 24;26(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04016-x. Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 35610649 Free PMC article.
-
Image-guided evaluation and monitoring of treatment response in patients with dry eye disease.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Jun;252(6):857-872. doi: 10.1007/s00417-014-2618-2. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24696045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in blood-brain barrier ICAM-1 expression and brain microglial activation after lambda-carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):H732-40. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00747.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16199477 Free PMC article.
-
Topical azithromycin and clarithromycin inhibit acute and chronic skin inflammation in sensitized mice, with apparent selectivity for Th2-mediated processes in delayed-type hypersensitivity.Inflammation. 2012 Feb;35(1):192-205. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9305-9. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 21336676
References
-
- AKAMATSU H., YAMAWAKI M., HORIO T. Effects of roxithromycin on adhesion molecules expressed on endothelial cells of the dermal microvasculature. J. Int. Med. Res. 2001;29:523–527. - PubMed
-
- ANDERSON R., FERNANDES A.C., EFTYCHIS H.E. Studies on the effects of ingestion of a single 500 mg oral dose of erythromycin stearate on leukocyte motility and transformation and on release in vitro of prostaglandin E2 by stimulated leukocytes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1984;14:41–50. - PubMed
-
- AZUMA A., LI Y., USUKI J., AOYAMA A., ENOMOTO T., KUDOH S. Fourteen-membered ring macrolides inhibit vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 messenger RNA induction preventing neutrophil-induced lung injury and fibrosis in bleomycin-challenged mice. Chest. 2001;120 Suppl:20S–22S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

