LIGHT is involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by inducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 in macrophages
- PMID: 15667572
- PMCID: PMC1782076
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.02004.x
LIGHT is involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by inducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 in macrophages
Abstract
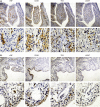
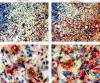
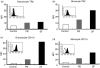
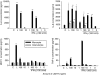
Macrophages play a crucial role in the perpetuation of inflammation and irreversible cartilage damage during the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). LIGHT (TNFSF14) and its receptor TR2 (TNFRSF14) are known to have pro-inflammatory activities in foam cells of atherosclerotic plaques. We tested a hypothesis that LIGHT and TR2 are involved in activation of monocyte/macrophages in RA synovium. Immunohistochemical analysis of RA synovial tissue samples revealed that both LIGHT and TR2 are expressed in CD68 positive macrophages. In contrast, synovial tissue samples from osteoarthritis (OA) patients failed to reveal the expression of LIGHT. Expression of TR2 in RA synovial macrophages was also detected using flow cytometry analysis. To identify the role of LIGHT in the functioning of macrophages in RA, we isolated macrophage enriched cells from RA synovial fluid and stimulated them with LIGHT. LIGHT induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8. These data indicate that LIGHT and TR2 expressed in macrophages are involved in the pathogenesis of RA by inducing the expression pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix degrading enzymes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of the dendritic cell-associated C-type lectin DC-SIGN by inflammatory matrix metalloproteinase-producing macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis synovium and interaction with intercellular adhesion molecule 3-positive T cells.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Feb;48(2):360-9. doi: 10.1002/art.10786. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12571844
-
The TNF superfamily member LIGHT contributes to survival and activation of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Jul;46(7):1063-70. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem063. Epub 2007 Apr 10. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17426140
-
Expression of CD147 on monocytes/macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: its potential role in monocyte accumulation and matrix metalloproteinase production.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(5):R1023-33. doi: 10.1186/ar1778. Epub 2005 Jun 23. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 16207318 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis, cytokines and hypoxia. What is the link?Saudi Med J. 2006 Nov;27(11):1642-9. Saudi Med J. 2006. PMID: 17106534 Review.
-
Interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor and their specific inhibitors.Eur Cytokine Netw. 1994 Nov-Dec;5(6):563-71. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1994. PMID: 7727689 Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction of monocytes with rheumatoid synovial cells is a key step in LIGHT-mediated inflammatory bone destruction.Immunology. 2009 Sep;128(1 Suppl):e315-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02965.x. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 19019090 Free PMC article.
-
CS-semi5 Inhibits NF-κB Activation to Block Synovial Inflammation, Cartilage Loss and Bone Erosion Associated With Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 9;12:655101. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655101. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34305585 Free PMC article.
-
Role of LIGHT in the pathogenesis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.World J Exp Med. 2017 May 20;7(2):49-57. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49. eCollection 2017 May 20. World J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 28589079 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of TNF family molecule LIGHT as a cytokine in the pathogenesis of hepatitis.J Clin Invest. 2006 Apr;116(4):1045-51. doi: 10.1172/JCI27083. Epub 2006 Mar 23. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16557300 Free PMC article.
-
Multilayered Computational Framework for Designing Peptide Inhibitors of HVEM-LIGHT Interaction.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Jul 18;128(28):6770-6785. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c02255. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38958133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cunnane G, Hummel KM, Muller-Ladner U, Gay RE, Gay S. Mechanism of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1998;46:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002;4:208–17. - PubMed
-
- Kinne RW, Brauer R, Stuhlmuller B, Palombo-Kinne E, Burmester GR. Macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2000;2:189–202. 10.1186/ar86. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mulherin D, Fitzgerald O, Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:115–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

