Depression during pegylated interferon-alpha plus ribavirin therapy: prevalence and prediction
- PMID: 15669887
- PMCID: PMC1615913
- DOI: 10.4088/jcp.v66n0106
Depression during pegylated interferon-alpha plus ribavirin therapy: prevalence and prediction
Abstract
Background: Interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) plus ribavirin is used to treat hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and is associated with a high rate of depression. Newer, pegylated preparations of IFN-alpha have a longer half-life, require once-per-week dosing, and may be associated with reduced neuropsychiatric burden. Limited data exist on depression during pegylated IFN-alpha therapy.
Method: Depressive symptoms were assessed using the Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) in 162 HCV-infected patients at baseline and after 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks of treatment with pegylated IFN alpha-2b (PEG IFN) plus weight-based (N = 86) versus standard dose (N = 76) ribavirin. Data were collected from March 2001 to April 2003.
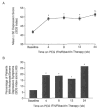
Results: Compared with baseline, mean SDS index scores were significantly increased by week 4 and remained elevated throughout the study. Thirty-nine percent of the sample experienced moderate to severe depressive symptoms (SDS index score > or = 60) at some point during PEG IFN/ribavirin therapy. Baseline depression scores significantly predicted severity of depressive symptoms during PEG IFN/ribavirin treatment (simple regression analysis: Y = 0.55X + 32.7, p < .0001). In addition, assignment to weight-based ribavirin treatment and history of depression were associated with increased likelihood of developing moderate to severe depressive symptoms (odds ratio [OR] = 2.7, 95% CI = 1.3 to 5.6, p < .01, and OR = 3.3, 95% CI = 1.3 to 8.1, p < .01, respectively).
Conclusions: Development of moderate to severe depressive symptoms occurred frequently during PEG IFN/ribavirin treatment and was predicted by baseline depression scores and higher doses of ribavirin. History of major depressive disorder was also a significant predictive factor, but only through association with elevated baseline depression status. All of these factors can be evaluated and addressed to limit neuropsychiatric morbidity during HCV treatment.
Figures

References
-
- Roitt I, Bostoff J, Male D. Immunology. New York, NY: Mosby; 1998.
-
- Zeuzem S. What is (cost) effective in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13:473–476. - PubMed
-
- Alter MJ, Kruszon-Moran D, Nainan OV, et al. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:556–562. - PubMed
-
- Alter HJ, Seeff LB. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin Liver Dis. 2000;20:17–35. - PubMed
-
- Miyaoka H, Otsubo T, Kamijima K, et al. Depression from interferon therapy in patients with hepatitis C [letter] Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156:1120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

