Functional antagonism of different G protein-coupled receptor kinases for beta-arrestin-mediated angiotensin II receptor signaling
- PMID: 15671181
- PMCID: PMC547874
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409532102
Functional antagonism of different G protein-coupled receptor kinases for beta-arrestin-mediated angiotensin II receptor signaling
Abstract
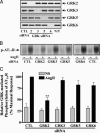
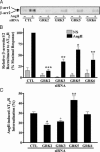
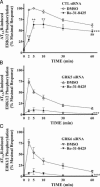
beta-arrestins bind to G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK)-phosphorylated seven transmembrane receptors, desensitizing their activation of G proteins, while concurrently mediating receptor endocytosis, and some aspects of receptor signaling. We have used RNA interference to assess the roles of the four widely expressed isoforms of GRKs (GRK 2, 3, 5, and 6) in regulating beta-arrestin-mediated signaling to the mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 by the angiotensin II type 1A receptor. Angiotensin II-stimulated receptor phosphorylation, beta-arrestin recruitment, and receptor endocytosis are all mediated primarily by GRK2/3. In contrast, inhibiting GRK 5 or 6 expression abolishes beta-arrestin-mediated ERK activation, whereas lowering GRK 2 or 3 leads to an increase in this signaling. Consistent with these findings, beta-arrestin-mediated ERK activation is enhanced by overexpression of GRK 5 and 6, and reciprocally diminished by GRK 2 and 3. These findings indicate distinct functional capabilities of beta-arrestins bound to receptors phosphorylated by different classes of GRKs.
Figures
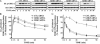
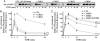

References
-
- Pierce, K. L., Premont, R. T. & Lefkowitz, R. J. (2002) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 639-650. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz, R. J. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 18677-18680. - PubMed
-
- Kohout, T. A. & Lefkowitz, R. J. (2003) Mol. Pharmacol. 63, 9-18. - PubMed
-
- Goodman, O. B., Jr., Krupnick, J. G., Santini, F., Gurevich, V. V., Penn, R. B., Gagnon, A. W., Keen, J. H. & Benovic, J. L. (1996) Nature 383, 447-450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

