Pregnane X receptor prevents hepatorenal toxicity from cholesterol metabolites
- PMID: 15671183
- PMCID: PMC548561
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409481102
Pregnane X receptor prevents hepatorenal toxicity from cholesterol metabolites
Abstract
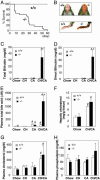
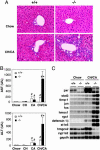
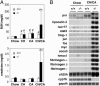
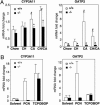
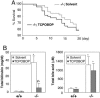
Efficient detoxification and clearance of cholesterol metabolites such as oxysterols, bile alcohols, and bile acids are critical for survival because they can promote liver and cardiovascular disease. We report here that loss of the nuclear xenobiotic receptor PXR (pregnane X receptor), a regulator of enterohepatic drug metabolism and clearance, results in an unexpected acute lethality associated with signs of severe hepatorenal failure when mice are fed with a diet that elicits accumulation of cholesterol and its metabolites. Induction of a distinct drug clearance program by a high-affinity ligand for the related nuclear receptor, the constitutive androstane receptor, does not overcome the lethality, indicating the unique requirement of PXR for detoxification. We propose that the PXR signaling pathway protects the body from toxic dietary cholesterol metabolites, and, by extension, PXR ligands may ameliorate human diseases such as cholestatic liver diseases and the associating acute renal failure.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cholesterol detoxification by the nuclear pregnane X receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2675-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500159102. Epub 2005 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15710871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Nuclear receptors constitutive androstane receptor and pregnane X receptor ameliorate cholestatic liver injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2063-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409794102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15684063 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnane X receptor (PXR) deficiency improves high fat diet-induced obesity via induction of fibroblast growth factor 15 (FGF15) expression.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 15;142:194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.07.019. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28756207
-
Identification of bile acid precursors as endogenous ligands for the nuclear xenobiotic pregnane X receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jan 7;100(1):223-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0237082100. Epub 2002 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12509506 Free PMC article.
-
Marine sponge steroids as nuclear receptor ligands.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Nov;33(11):591-601. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23000093 Review.
-
Pregnane X receptor: promiscuous regulator of detoxification pathways.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(3):478-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.08.017. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17188925 Review.
Cited by
-
Pregnane X receptor and natural products: beyond drug-drug interactions.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2006 Dec;2(6):847-57. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2.6.847. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 17125405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tumor suppressor TERE1 (UBIAD1) prenyltransferase regulates the elevated cholesterol phenotype in castration resistant prostate cancer by controlling a program of ligand dependent SXR target genes.Oncotarget. 2013 Jul;4(7):1075-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1103. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23919967 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Receptor PXR in Drug-Induced Hypercholesterolemia.Cells. 2022 Jan 18;11(3):313. doi: 10.3390/cells11030313. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol detoxification by the nuclear pregnane X receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2675-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500159102. Epub 2005 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15710871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cytochrome P450 and gene activation--from pharmacology to cholesterol elimination and regression of atherosclerosis.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Sep;64(9):841-50. doi: 10.1007/s00228-008-0515-5. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18633604 Review.
References
-
- Russell, D. W. (2003) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 137-174. - PubMed
-
- Koopen, N. R., Muller, M., Vonk, R. J., Zimniak, P. & Kuipers, F. (1998) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1408, 1-17. - PubMed
-
- Elferink, R. O. & Groen, A. K. (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1586, 129-145. - PubMed
-
- Chawla, A., Repa, J. J., Evans, R. M. & Mangelsdorf, D. J. (2001) Science 294, 1866-1870. - PubMed
-
- Xie, W. & Evans, R. M. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 37739-37742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

