Soluble lumican glycoprotein purified from human amniotic membrane promotes corneal epithelial wound healing
- PMID: 15671272
- PMCID: PMC1317307
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.04-1014
Soluble lumican glycoprotein purified from human amniotic membrane promotes corneal epithelial wound healing
Abstract
Purpose: To purify and characterize the glycoprotein lumican, isolated from human amniotic membrane (AM), and to examine its efficacy in treating corneal epithelium debridement.
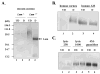
Methods: An affinity-purified, anti-human lumican antibody-conjugated protein A Sepharose column was used to purify soluble lumican protein from human AM. The purified AM lumican was characterized by two-dimensional and SDS gel electrophoresis, plus Western blot analysis with anti-lumican antibody. The effects of lumican on corneal epithelial wound healing were examined in an organ culture mouse eye model.
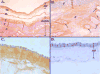
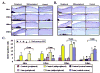
Results: Lumican was found to be abundantly present in the stroma of human AM. It was extracted from the AM by isotonic, 1 M NaCl, and 4 M guanidine HCl solutions, suggesting that it is present in both the soluble and matrix-bound states. In two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, the 50-kDa human amniotic lumican purified by antibody-conjugated affinity chromatography migrated in a smear between pH 3.0 and 6.0. After endo-beta-galactosidase digestion, it existed as a single core protein at pH 6.0, suggesting that native human amniotic lumican is a glycoprotein with short sugar moiety. Addition of purified human AM lumican to cultured medium promoted re-epithelialization and enhanced cell proliferation of wild-type mouse corneal epithelial cells in an organ culture. In lumican-knockout (lum(-/-)) mice, the effect of human lumican on promoting corneal epithelial wound healing was even more dramatic than in wild-type mice.
Conclusions: The diversified functions of lumican include modulation of epithelial cells in wound healing and serving as an extracellular matrix component. Administration of lumican may be beneficial for treating epithelial defects in the cornea and other tissues.
Figures




References
-
- Funderburgh JL, Funderburgh ML, Mann MM, Conrad GW. Arterial lumican: properties of a corneal-type keratan sulfate proteoglycan from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:24773–24777. - PubMed
-
- Funderburgh JL, Caterson B, Conrad GW. Distribution of proteoglycans antigenically related to corneal keratan sulfate proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:11634–11640. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo RV, Murdoch AD. Proteoglycan of the extracellular environment: clues from the gene and protein side offer novel perspectives in molecular diversity and function. FASEB J. 1996;10:598–614. - PubMed
-
- Knudson CB, Knudson W. Cartilage proteoglycans. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2001;12:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Ying S, Shiraishi A, Kao CW, et al. Characterization and expression of the mouse lumican gene. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30306–30313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

