N-linked oligosaccharides affect the enzymatic activity of CD39: diverse interactions between seven N-linked glycosylation sites
- PMID: 15673609
- PMCID: PMC1073650
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0886
N-linked oligosaccharides affect the enzymatic activity of CD39: diverse interactions between seven N-linked glycosylation sites
Abstract
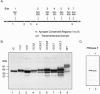
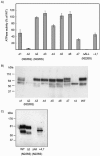
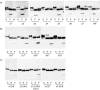
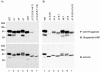
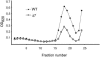
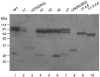
Rat CD39, a membrane-bound ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase that hydrolyzes extracellular nucleoside tri- and diphosphates, has seven potential N-glycosylation sites at asparagine residues 73, 226, 291, 333, 375, 429, and 458. To determine their roles in the structure and function of CD39, we mutated these sites individually or in combination by replacing asparagine with serine or glutamine and analyzed the surface expression and the enzymatic activity of the mutants. The results indicate that rat CD39 can be glycosylated at all seven sites when expressed in COS7 cells. Glycosylation sites 73 at the N terminus, 333 in the middle, and 429 and 458 at the C terminus were principally required for cell surface appearance of enzymatically active CD39. Whereas deletion of these sites individually had modest effects on surface ATPase activity, some double deletions of these sites had major effects on both surface activity and expression. The importance of these N-glycosylation sites is recognizable in other members of the ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase family.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mammalian plasma membrane ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1, CD39, is not active intracellularly. The N-glycosylation state of CD39 correlates with surface activity and localization.J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 2;276(44):41518-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104415200. Epub 2001 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11546800
-
Distinctive roles of endoplasmic reticulum and golgi glycosylation in functional surface expression of mammalian E-NTPDase1, CD39.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 May 25;1723(1-3):143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.01.010. Epub 2005 Feb 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15777625
-
Glycosylation is essential for functional expression of a human brain ecto-apyrase.Biochemistry. 1999 Feb 2;38(5):1509-16. doi: 10.1021/bi9821768. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 9931016
-
Beyond ecto-nucleotidase: CD39 defines human Th17 cells with CD161.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Sep;11(3):317-9. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9457-4. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26059452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Ecto-nucleotidases of ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase family: structure, localization and functional significance].Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2010 May-Jun;82(3):5-17. Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2010. PMID: 21328873 Review. Ukrainian.
Cited by
-
Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases.Purinergic Signal. 2012 Sep;8(3):437-502. doi: 10.1007/s11302-012-9309-4. Epub 2012 May 4. Purinergic Signal. 2012. PMID: 22555564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GDA1_CD39 superfamily: NTPDases with diverse functions.Purinergic Signal. 2011 Mar;7(1):21-45. doi: 10.1007/s11302-010-9214-7. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Purinergic Signal. 2011. PMID: 21484095 Free PMC article.
-
Sweet regulation - The emerging immunoregulatory roles of hexoses.J Adv Res. 2025 Mar;69:361-379. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.014. Epub 2024 Apr 15. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38631430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATPe Dynamics in Protozoan Parasites. Adapt or Perish.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 27;10(1):16. doi: 10.3390/genes10010016. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30591699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient changes in the localization and activity of ecto-nucleotidases in rat hippocampus following lipopolysaccharide treatment.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2007 Aug;25(5):275-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2007.05.007. Epub 2007 May 17. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17576046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames, B. N. (1966). Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatases. Methods Enzymol 8, 115–117.
-
- Biederbick, A., Rose, S., and Elsasser, H. P. (1999). A human intracellular apyrase-like protein, LALP70, localizes to lysosomal/autophagic vacuoles. J. Cell Sci. 112, 2473–2484. - PubMed
-
- Bigonnesse, F., Levesque, S. A., Kukulski, F., Lecka, J., Robson, S. C., Fernandes, M. J., and Sevigny, J. (2004). Cloning and characterization of mouse nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-8. Biochemistry 43, 5511–5519. - PubMed
-
- Braun, N., Sevigny, J., Robson, S. C., Enjyoji, K., Guckelberger, O., Hammer, K., Di Virgilio, F., and Zimmermann, H. (2000). Assignment of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1/cd39 expression to microglia and vasculature of the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 4357–4366. - PubMed
-
- Enjyoji, K., et al. (1999). Targeted disruption of cd39/ATP diphosphohydrolase results in disordered hemostasis and thromboregulation. Nat. Med. 5, 1010–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

