Differential regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor- and AMPA receptor-mediated dendritic Ca2+ signals by presynaptic and postsynaptic activity in hippocampal interneurons
- PMID: 15673681
- PMCID: PMC6725617
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4388-04.2005
Differential regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor- and AMPA receptor-mediated dendritic Ca2+ signals by presynaptic and postsynaptic activity in hippocampal interneurons
Abstract
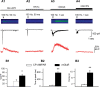
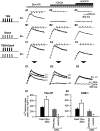
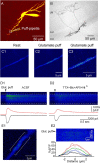
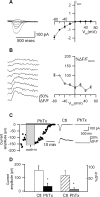
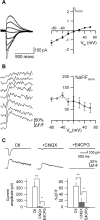
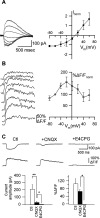
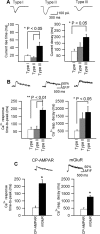
Calcium plays a crucial role as a ubiquitous second messenger and has a key influence in many forms of synaptic plasticity in neurons. The spatiotemporal properties of dendritic Ca2+ signals in hippocampal interneurons are relatively unexplored. Here we use two-photon calcium imaging and whole-cell recordings to study properties of dendritic Ca2+ signals mediated by different glutamate receptors and their regulation by synaptic activity in oriens/alveus (O/A) interneurons of rat hippocampus. We demonstrate that O/A interneurons express Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors (CP-AMPARs) providing fast Ca2+ signals. O/A cells can also coexpress CP-AMPARs, Ca2+-impermeable AMPARs (CI-AMPARs), and group I/II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) (including mGluR1a), in the same cell. CI-AMPARs are often associated with mGluRs, resulting in longer-lasting Ca2+ signals than CP-AMPAR-mediated responses. Finally, CP-AMPAR- and mGluR-mediated Ca2+ signals demonstrate distinct voltage dependence and are differentially regulated by presynaptic and postsynaptic activity: weak synaptic stimulation produces Ca2+ signals mediated by CP-AMPARs, whereas stronger stimulation, or weak stimulation coupled with postsynaptic depolarization, recruits Ca2+ signals mediated by mGluRs. Our results suggest that differential activation of specific glutamate receptor-mediated Ca2+ signals within spatially restricted dendritic microdomains may serve distinct signaling functions and endow oriens/alveus interneurons with multiple forms of Ca2+-mediated synaptic plasticity. Specific activation of mGluR-mediated Ca2+ signals by coincident presynaptic and postsynaptic activity fulfills the conditions for Hebbian pairing and likely underlies their important role in long-term potentiation induction at O/A interneuron synapses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptically activated calcium responses in dendrites of hippocampal oriens-alveus interneurons.J Neurophysiol. 2001 Apr;85(4):1603-13. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.85.4.1603. J Neurophysiol. 2001. PMID: 11287484
-
Induction of Anti-Hebbian LTP in CA1 Stratum Oriens Interneurons: Interactions between Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and M1 Muscarinic Receptors.J Neurosci. 2015 Oct 7;35(40):13542-54. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0956-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26446209 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic calcium nonlinearities switch the direction of synaptic plasticity in fast-spiking interneurons.J Neurosci. 2014 Mar 12;34(11):3864-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2253-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24623765 Free PMC article.
-
Induction and expression rules of synaptic plasticity in hippocampal interneurons.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Apr;60(5):720-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.016. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21195098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of distinct glutamate receptors in induction of anti-Hebbian long-term potentiation.J Physiol. 2008 Mar 15;586(6):1481-6. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.148064. Epub 2008 Jan 10. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18187472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two-photon Calcium Imaging in Neuronal Dendrites in Brain Slices.J Vis Exp. 2018 Mar 15;(133):56776. doi: 10.3791/56776. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29608159 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic inhibition mediated by O-LM and bistratified interneurons in the hippocampus.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2014 Sep 30;6:23. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00023. eCollection 2014. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25324774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Calcium-Permeable AMPARs in Long-Term Potentiation at Principal Neurons in the Rodent Hippocampus.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2018 Nov 22;10:42. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00042. eCollection 2018. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30524263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological diversity and connectivity of hippocampal interneurons.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Sep;373(3):619-641. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2882-2. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 30084021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spike-timing dependent plasticity in inhibitory circuits.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2010 Jun 21;2:8. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2010.00008. eCollection 2010. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21423494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Mulvihill E, McIlhinney RA, Somogyi P (1993) The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1 alpha) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron 11: 771-787. - PubMed
-
- Bowie D, Mayer ML (1995) Inward rectification of both AMPA and kainate subtype glutamate receptors generated by polyamine-mediated ion channel block. Neuron 15: 453-462. - PubMed
-
- Carmant L, Woodhall G, Ouardouz M, Robitaille R, Lacaille JC (1997) Interneuron-specific Ca2+ responses linked to metabotropic and ionotropic glutamate receptors in rat hippocampal slices. Eur J Neurosci 9: 1625-1635. - PubMed
-
- Chuang SC, Bianchi R, Wong RK (2000) Group I mGluR activation turns on a voltage-gated inward current in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol 83: 2844-2853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
