Rapid creation of BAC-based human artificial chromosome vectors by transposition with synthetic alpha-satellite arrays
- PMID: 15673719
- PMCID: PMC548352
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki207
Rapid creation of BAC-based human artificial chromosome vectors by transposition with synthetic alpha-satellite arrays
Abstract
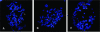
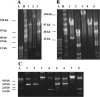
Efficient construction of BAC-based human artificial chromosomes (HACs) requires optimization of each key functional unit as well as development of techniques for the rapid and reliable manipulation of high-molecular weight BAC vectors. Here, we have created synthetic chromosome 17-derived alpha-satellite arrays, based on the 16-monomer repeat length typical of natural D17Z1 arrays, in which the consensus CENP-B box elements are either completely absent (0/16 monomers) or increased in density (16/16 monomers) compared to D17Z1 alpha-satellite (5/16 monomers). Using these vectors, we show that the presence of CENP-B box elements is a requirement for efficient de novo centromere formation and that increasing the density of CENP-B box elements may enhance the efficiency of de novo centromere formation. Furthermore, we have developed a novel, high-throughput methodology that permits the rapid conversion of any genomic BAC target into a HAC vector by transposon-mediated modification with synthetic alpha-satellite arrays and other key functional units. Taken together, these approaches offer the potential to significantly advance the utility of BAC-based HACs for functional annotation of the genome and for applications in gene transfer.
Figures
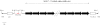

References
-
- Lee C., Wevrick R., Fisher R.B., Ferguson-Smith M.A., Lin C.C. Human centromeric DNAs. Hum. Genet. 1997;100:291–304. - PubMed
-
- Rudd M.K., Schueler M.G., Willard H.F. Characterization and functional annotation of human centromeres. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2004;68:141–150. - PubMed
-
- Rudd M.K., Willard H.F. Analysis of the centromeric regions of the human genome assembly. Trends Genet. 2004;20:529–533. - PubMed
-
- Pluta A.F., Mackay A.M., Ainsztein A.M., Goldberg I.G., Earnshaw W.C. The centromere: hub of chromosomal activities. Science. 1995;270:1591–1594. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan B.A., Blower M.D., Karpen G.H. Determining centromere identity: cyclical stories and forking paths. Nature Rev. Genet. 2001;2:584–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

