Clinical pharmacokinetics of nelfinavir and its metabolite M8 in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive and HIV-hepatitis C virus-coinfected subjects
- PMID: 15673746
- PMCID: PMC547212
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.2.643-649.2005
Clinical pharmacokinetics of nelfinavir and its metabolite M8 in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive and HIV-hepatitis C virus-coinfected subjects
Abstract
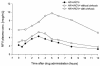
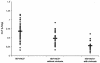
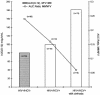
In order to evaluate the potential risk of nelfinavir (NFV) accumulation in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-hepatitis C virus (HCV)-coinfected patients with liver disease, we investigated the concentrations of NFV and M8, the active metabolite of NFV, in plasma HIV-positive (HIV+) patients coinfected with HCV. A total of 119 HIV+ subjects were included in our study: 67 HIV+ patients, 32 HIV+ and HCV-positive (HCV+) patients without cirrhosis, and 20 HIV+ and HCV+ patients with cirrhosis. Most of the enrolled patients (chronically treated) were taking NFV at the standard dosage of 1,250 mg twice a day. To assay plasma NFV and M8 concentrations, patients underwent serial plasma samplings during the dosing interval at steady state. Plasma NFV and M8 concentrations were measured simultaneously by a high-performance liquid chromatography method with UV detection. The HIV+ and HCV+ patients with and without cirrhosis had significantly lower NFV oral clearances than the HIV+ and HCV-negative individuals (28 and 58% lower, respectively; P < 0.05), which translated into higher areas under the concentration-time curves for cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients. The NFV absorption rate was significantly lower in cirrhotic patients, resulting in a longer time to the maximum concentration in serum. The mean ratios of the M8 concentration/NFV concentration were significantly lower (P < 0.05) in HIV+ and HCV+ subjects with cirrhosis (0.06 +/- 0.074) than in the subjects in the other two groups. The mean ratios for M8 and NFV were not statistically different between HIV+ and HCV-negative patients (0.16 +/- 0.13) and HIV+ and HCV+ patients without cirrhosis (0.24 +/- 0.17), but the interpatient variability was high. Our results indicate that the pharmacokinetics of NFV and M8 are altered in HIV+ and HCV+ patients, especially those with liver cirrhosis. Therefore, there may be a role for therapeutic drug monitoring in individualizing the NFV dosage in HIV-HCV-coinfected patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bayesian parameter estimates of nelfinavir and its active metabolite, hydroxy-tert-butylamide, in infants perinatally infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Feb;49(2):525-35. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.2.525-535.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15673728 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nelfinavir+M8 plasma levels determined with an ELISA test in HIV infected patients with or without HCV and/or HBV coinfection: the VIRAKINETICS II study.Curr HIV Res. 2009 May;7(3):293-301. doi: 10.2174/157016209788347967. Curr HIV Res. 2009. PMID: 19442125
-
Pharmacokinetics of Increased Nelfinavir Plasma Concentrations in Women During Pregnancy and Postpartum.J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;59(3):386-393. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1331. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30358179 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Elevated plasma concentrations of protease inhibitors and nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors in patients coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis B or C: case series and literature review.Pharmacotherapy. 2005 Aug;25(8):1068-72. doi: 10.1592/phco.2005.25.8.1068. Pharmacotherapy. 2005. PMID: 16207097 Review.
-
Nelfinavir.2017 Sep 1. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2017 Sep 1. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643634 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of β-carotene supplementation on the pharmacokinetics of nelfinavir and its active metabolite M8 in HIV-1-infected patients.Molecules. 2012 Jan 12;17(1):688-702. doi: 10.3390/molecules17010688. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22241465 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Management and treatment of hepatitis C virus in patients with HIV and hepatitis C virus coinfection: A practical guide for health care professionals.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2007 Sep;18(5):293-303. doi: 10.1155/2007/631054. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 18923731 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of nelfinavir in HIV-1-infected pregnant and nonpregnant women.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;62(3):309-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02669.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16934047 Free PMC article.
-
Management and Treatment of Hepatitis C: Are There Still Unsolved Problems and Unique Populations?Viruses. 2021 Jun 1;13(6):1048. doi: 10.3390/v13061048. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34205966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Liver Disease on Hepatic Transporter Expression and Function.J Pharm Sci. 2017 Sep;106(9):2282-2294. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.04.053. Epub 2017 Apr 30. J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28465155 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aube, C., F. Oberti, N. Korali, M. A. Namour, D. Loisel, J. Y. Tanguy, E. Valsesia, C. Pilette, M. C. Rousselet, P. Bedossa, H. Rifflet, M. Y. Maiga, D. Penneau-Fontbonne, C. Caron, and P. Cales. 1999. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 30:472-478. - PubMed
-
- Branch, R. A. 1998. Drugs in liver disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 64:462-464. - PubMed
-
- Brouwer, K. L. R., G. E. Dukes, and J. R. Powell. 1996. Influence of liver function on drug disposition. .In W. E. Evans, J. J. Schentag, and W. J. Jusko (ed.), Applied pharmacokinetics, principles of therapeutic drug monitoring. Applied Therapeutics, Vancouver, Wash.
-
- Burger, D., P. Hugen, P. Reiss, I. Gyssens, M. Schneider, F. Kroon, G. Schreij, K. Brinkman, C. Richter, J. Prins, R. Aarnoutse, J. Lange, and the ATHENA Cohort Study Group. 2003. Therapeutic drug monitoring of nelfinavir and indinavir in treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected individuals. AIDS 17:1157-1165. - PubMed
-
- Colli, A., M. Fraquelli, B. Marino, E. Zuccoli, and D. Conte. 2003. Severe liver fibrosis or cirrhosis: accuracy of US for detection—analysis of 300 cases. Radiology 227:89-94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

