Ultrastructural evaluation of the radioprotective effects of melatonin against X-ray-induced skin damage in Albino rats
- PMID: 15676032
- PMCID: PMC2517401
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2005.00412.x
Ultrastructural evaluation of the radioprotective effects of melatonin against X-ray-induced skin damage in Albino rats
Abstract
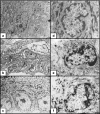
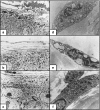
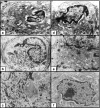
Our knowledge about the radioprotective effects of melatonin against X-ray-induced skin damage is still lacking. To examine these effects, an animal model of 60 Albino rats was used. The animals were divided into five groups: Group 1, nonirradiated; Group 2, X-ray irradiated (XRI, 8 Gy); Group 3, XRI pretreated with solvent (ethanol and phosphate-buffered saline); Group 4, nonirradiated group treated with melatonin; and Group 5, XRI pretreated with melatonin. The skin was evaluated for ultrastructural changes using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When compared to the nonirradiated skin (Groups 1 and 4), XRI skin (Groups 2 and 3) showed features of both cell injury and increased metabolic activity. The former included changes such as condensation of the nuclei, vacuolization of the cytoplasm, dilatation of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, swelling of the mitochondria with cristolysis, destruction of the ribosomes and intermediate filaments, fragmentation of the keratohyaline granules and loss of the irregularity of the basal cell borders. The central cells of the sebaceous gland alveoli had larger irregular nuclei and few lipid droplets in their cytoplasm. The hair follicle cells had heterochromatic nuclei and less electron dense cytoplasm containing few complements of the organelles. The features of increased metabolic activity included increased euchromatin, irregularity of the nuclear membrane and increased branching of the melanocytes. Also, an increased number of the Birbeck granules were seen in the Langerhans cells. When compared to the irradiated skin (Groups 2 and 3), these changes were mild or absent in the skin of XRI animals pretreated with melatonin (Group 5). The ability of melatonin to minimize the injurious effects of XRI suggests a radioprotective role. The clinical ramifications of these observations warrant further studies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Morphological evaluation of the radioprotective effects of melatonin against X-ray-induced early and acute testis damage in Albino rats: an animal model.Int J Exp Pathol. 2006 Jun;87(3):237-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00480.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16709232 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin and roentgen irradiation-induced acute radiation enteritis in Albino rats: an animal model.Cell Biol Int. 2008 Nov;32(11):1353-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Aug 13. Cell Biol Int. 2008. PMID: 18762261
-
Ultrastructural clues for the potent therapeutic effect of melatonin on aging skin in pinealectomized rats.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;20(6):605-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2006.00439.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17109654
-
Melatonin and roentgen irradiation of the testis.Fertil Steril. 2006 Sep;86(3):750-2. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.02.094. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Fertil Steril. 2006. PMID: 16854416
-
Melatonin as a radioprotective agent: a review.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Jul 1;59(3):639-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.02.006. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 15183467 Review.
Cited by
-
Ulva lactuca polysaccharides prevent Wistar rat breast carcinogenesis through the augmentation of apoptosis, enhancement of antioxidant defense system, and suppression of inflammation.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017 Feb 27;9:67-83. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S125165. eCollection 2017. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017. PMID: 28280387 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of tea saponins to relive oxidative stress and immune suppression in chickens.Poult Sci. 2017 Sep 1;96(9):3058-3067. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex127. Poult Sci. 2017. PMID: 28633386 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Melatonin on the Skin: Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4948. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194948. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin induces a stimulatory action on the scrotal skin components of Soay ram in the non-breeding season.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 23;10(1):10154. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67103-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32576871 Free PMC article.
-
The biochemical and morphological alterations following administration of melatonin, retinoic acid and Nigella sativa in mammary carcinoma: an animal model.Int J Exp Pathol. 2005 Dec;86(6):383-96. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2005.00448.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16309544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archambeau JO, Ines A, et al. Response of swine skin microvasculature to acute single exposures of X rays: quantification of endothelial changes. Radiat. Res. 1984;98(1):37–51. - PubMed
-
- Beltran G, Stuckey WJ. Nuclear lobulation and cytoplasmic fibrils in leukemic plasma cells. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1972;58(2):159–164. - PubMed
-
- Berry RJ, Mole RH, et al. Skin response to X-irradiation in the guinea-pig. Int. J. Radiat Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1976;30(6):535–541. - PubMed
-
- Bessis M, Breton-Gorius J. Role of the cytoplasm fibrils in lobulation of the cell nucleus (formation of Rieder's cells) C R. Acad. Sci. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. D. 1965;261(5):1392–1393. - PubMed
-
- Cesarini JP. Recent advances in the ultrastructure of malignant melanoma. Rev. Eur. Etud. Clin. Biol. 1971;16(4):316–322. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

