Individualized quality of life, standardized quality of life, and distress in patients undergoing a phase I trial of the novel therapeutic Reolysin (reovirus)
- PMID: 15676074
- PMCID: PMC548292
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-3-7
Individualized quality of life, standardized quality of life, and distress in patients undergoing a phase I trial of the novel therapeutic Reolysin (reovirus)
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the individualized and standardized quality of life (QL) and psychological distress of patients participating in a Phase I trial of the novel therapeutic reovirus (Reolysin).
Methods: 16 patients with incurable metastatic cancer were interviewed prior to being accepted into the phase I trial with a semi-structured expectations interview, the Schedule for the Evaluation of Individual Quality of Life--Direct Weighting (SEIQoL-DW), the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30), the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI), the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and the Spiritual Health Inventory (SHI).
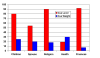
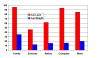
Results: Patients were able to complete all measures. They felt hopeful and excited about the trial, with about two thirds hoping for disease regression and one third hoping for a cure. The most commonly spontaneously nominated areas of QL were family relationships, activities and friends, and the overall SEIQoL mean index score was 69. Health was nominated by only 38% of the sample. Scores on the SEIQoL were correlated with global QL on the EORTC QLQ C-30. Scores on the BDI and BSI were lower than reported for similar populations, and on the SHI scores were similar to other samples. Global QL on the EORTC QLQ C-30 and depression scores were associated with time to death in the nine patients who had died at the time of writing.
Conclusions: Individualized QL is easy to assess in seriously ill cancer patients, provides useful information relative to each individual, and is related to standard QL measures. Repeated assessment of individualized QL of patients in Phase I trials would be a useful addition to the research.
Figures
References
-
- Spilker B. In: Quality of Life Assessments in Clinical Trials. Spilker B, editor. New York, Raven Press; 1990.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical