A methylation sensitive dot blot assay (MS-DBA) for the quantitative analysis of DNA methylation in clinical samples
- PMID: 15677535
- PMCID: PMC1770569
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2004.021147
A methylation sensitive dot blot assay (MS-DBA) for the quantitative analysis of DNA methylation in clinical samples
Abstract
Background: There is increasing interest in DNA methylation and in its implication in transcriptional gene silencing, a phenomenon commonly seen in human cancer.
Aims: To develop a new method that would allow quantitative DNA methylation analysis in a large range of clinical samples, independently of the processing protocol.
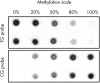
Methods: A methylation sensitive dot blot assay (MS-DBA) was developed, which is quantitative and combines bisulfite modification, PCR amplification using primers without CpG sites, and dot blot analysis with two probes specific for methylated and unmethylated DNA.
Results: The established method was used to study methylation of the hTERT, APC, and p16 promoter regions in microdissected, formalin fixed and paraffin wax embedded tissues.
Conclusions: MS-DBA is a sensitive, specific, and quantitative approach to analyse DNA methylation in a variety of frozen or fixed tissues. Moreover, MS-DBA is rapid, easy to perform, and permits the screening of a large panel of samples in one experiment. Thus, MS-DBA can facilitate the routine analysis of DNA methylation in all types of clinical samples.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Methylation-sensitive single-strand conformation analysis: a rapid method to screen for and analyze DNA methylation.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;287:181-93. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-828-5:181. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15273412
-
Methylation of APC, TIMP3, and TERT: a new predictive marker to distinguish Barrett's oesophagus patients at risk for malignant transformation.J Pathol. 2006 Jan;208(1):100-7. doi: 10.1002/path.1884. J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16278815
-
Methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction.Methods Mol Med. 2005;113:279-91. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-916-8:279. Methods Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15968111
-
Limitations and advantages of MS-HRM and bisulfite sequencing for single locus methylation studies.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2010 Jul;10(5):575-80. doi: 10.1586/erm.10.46. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2010. PMID: 20629507 Review.
-
Quantitative detection of DNA methylation states in minute amounts of DNA from body fluids.Methods. 2010 Nov;52(3):242-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.03.008. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Methods. 2010. PMID: 20362673 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic alteration of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 promoter occurs early in the carcinogenesis of Barrett's esophagus.Cancer Sci. 2008 Jan;99(1):46-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00663.x. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18005197 Free PMC article.
-
The common bisulfite-conversion-based techniques to analyze DNA methylation in human cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03405-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38982390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and methylation pattern of p16 in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2010 Mar;16(1):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s12253-009-9178-5. Epub 2009 May 23. Pathol Oncol Res. 2010. PMID: 19466588
-
Diagnostic Value of Methylated Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase in Human Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2015 Dec 24;5:296. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00296. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26734575 Free PMC article.
-
hTERT methylation is necessary but not sufficient for telomerase activity in colorectal cells.Oncol Lett. 2011 Nov;2(6):1257-1260. doi: 10.3892/ol.2011.386. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Oncol Lett. 2011. PMID: 22848298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2002;3:415–28. - PubMed
-
- Jones PA, Laird PW. Cancer epigenetics comes of age. Nat Genet 1999;21:163–7. - PubMed
-
- Laird PW. The power and the promise of DNA methylation markers. Nat Rev Cancer 2003;3:253–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
