Infliximab improves signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis: results of the IMPACT 2 trial
- PMID: 15677701
- PMCID: PMC1755609
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.032268
Infliximab improves signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis: results of the IMPACT 2 trial
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate further in a phase III, double blind trial the efficacy of infliximab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), as observed in the smaller IMPACT trial.
Methods: 200 patients with active PsA unresponsive to previous treatment were randomised to infusions of infliximab 5 mg/kg or placebo at weeks 0, 2, 6, 14, and 22. Patients with inadequate response entered early escape at week 16. The primary measure of clinical response was ACR20. Other measures included Psoriatic Arthritis Response Criteria (PsARC), Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), and dactylitis and enthesopathy assessments.
Results: At week 14, 58% of patients receiving infliximab and 11% of those receiving placebo achieved an ACR20 response and 77% of infliximab patients and 27% of placebo patients achieved PsARC (both p<0.001). Among the 85% of patients with at least 3% body surface area psoriasis involvement at baseline, 53/83 (64%) patients receiving infliximab had at least 75% improvement in PASI compared with 2/87 (2%) patients receiving placebo at week 14 (p<0.001). These therapeutic effects were maintained through the last evaluation (week 24). Fewer infliximab patients than placebo patients had dactylitis at week 14 (18% v 30%; p = 0.025) and week 24 (12% v 34%; p<0.001). Fewer infliximab patients (22%) than placebo patients (34%) had active enthesopathy at week 14 (p = 0.016); corresponding figures at week 24 were 20% and 37% (p = 0.002). Infliximab was generally well tolerated, with a similar incidence of adverse events in each group.
Conclusions: Infliximab 5 mg/kg through 24 weeks significantly improved active PsA, including dactylitis and enthesopathy, and associated psoriasis.
Figures
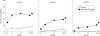
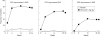
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

