Effects of diltiazem and nifedipine on transient outward and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier potassium currents in human atrial myocytes
- PMID: 15678082
- PMCID: PMC1576039
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706113
Effects of diltiazem and nifedipine on transient outward and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier potassium currents in human atrial myocytes
Abstract
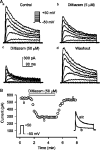
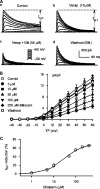
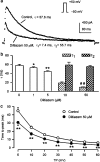
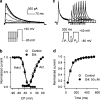
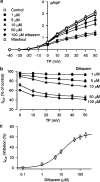
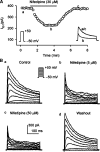
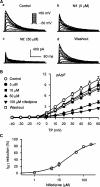
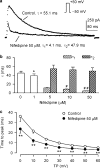
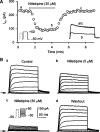
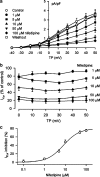
1. It is unknown whether the widely used L-type Ca(2+) channel antagonists diltiazem and nifedipine would block the repolarization K(+) currents, transient outward current (I(to1)) and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier K(+) current (I(Kur)), in human atrium. The present study was to determine the effects of diltiazem and nifedipine on I(to1) and I(Kur) in human atrial myocytes with whole-cell patch-clamp technique. 2. It was found that diltiazem substantially inhibited I(to1) in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC(50) of 29.2+/-2.4 microM, and nifedipine showed a similar effect (IC(50)=26.8+/-2.1 muM). The two drugs had no effect on voltage-dependent kinetics of the current; however, they accelerated I(to1) inactivation significantly, suggesting an open channel block. 3. In addition, diltiazem and nifedipine suppressed I(Kur) in a concentration-dependent manner (at +50 mV, IC(50)=11.2+/-0.9 and 8.2+/-0.8 microM, respectively). These results indicate that the Ca(2+) channel blockers diltiazem and nifedipine substantially inhibit I(to1) and I(Kur) in human atrial myocytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit transient outward and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier K+currents and Na+current in human atrial myocytes.Cardiovasc Res. 2009 Feb 1;81(2):286-93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn322. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19029136
-
Inhibition of ultra-rapid delayed rectifier K+ current by verapamil in human atrial myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004 Feb;36(2):257-63. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2003.11.003. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 14871553
-
Effects of chromanol 293B on transient outward and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier potassium currents in human atrial myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003 Mar;35(3):293-300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(03)00007-5. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12676544
-
Pharmacology of cardiac potassium channels.Adv Pharmacol. 2010;59:93-134. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(10)59004-5. Adv Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20933200 Review.
-
Ultra-rapid delayed rectifier channels: molecular basis and therapeutic implications.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Mar 1;89(4):776-85. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq398. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21159668 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of voltage-gated K+ and Na+ channels in gastric epithelial cell migration.Mol Cell Biochem. 2008 Jan;308(1-2):219-26. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9631-2. Epub 2007 Nov 3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17978865
-
Transient outward K+ current can strongly modulate action potential duration and initiate alternans in the human atrium.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Mar 1;316(3):H527-H542. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00251.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30576220 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the antifungal antibiotic clotrimazole on human cardiac repolarization potassium currents.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;147(3):289-97. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706590. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16341233 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibitory Effects of Ca2+ Channel Blocker Nifedipine on Rat Kv2.1 Potassium Channels.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 20;10(4):e0124602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124602. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25893973 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of multiple ion channels in cultured human cardiac fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 6;4(10):e7307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007307. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19806193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CALMELS T.P., FAIVRE J.F., CHEVAL B., JAVRE J.L., ROUANET S., BRIL A. hKv4.3 channel characterization and regulation by calcium channel antagonists. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001;281:452–560. - PubMed
-
- COURTEMANCHE M., RAMIREZ R.J., NATTEL S. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: insights from a mathematical model. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;275:H301–H321. - PubMed
-
- COURTEMANCHE M., RAMIREZ R.J., NATTEL S. Ionic targets for drug therapy and atrial fibrillation-induced electrical remodeling: insights from a mathematical model. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999;42:477–489. - PubMed
-
- DE LEEUW P.W., BIRKENHAGER W.H. The effects of calcium channel blockers on cardiovascular outcomes: a review of randomised controlled trials. Blood Press. 2002;11:71–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

