Relationship between brain serotonin transporter binding, plasma concentration and behavioural effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- PMID: 15678084
- PMCID: PMC1576050
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706108
Relationship between brain serotonin transporter binding, plasma concentration and behavioural effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Abstract
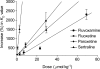
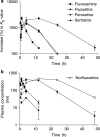
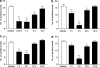
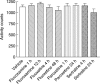
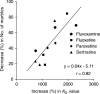
1. The present study was undertaken to characterise the relationship between in vivo brain serotonin transporter (SERT) binding, plasma concentration and pharmacological effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in mice. Oral administration of fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, paroxetine and sertraline at pharmacologically relevant doses exerted dose- and time-dependent binding activity of brain SERT as revealed by significant increases in KD for specific [3H]paroxetine binding, and the in vivo SERT-binding potency was in the order of paroxetine>>fluoxetine, sertraline>fluvoxamine. 2. The time courses of brain SERT binding by SSRIs in mice were mostly in parallel to those of their plasma concentrations. Also, norfluoxetine (active metabolite) has been suggested to contribute largely to the long-lasting binding activity of brain SERT after the fluoxetine administration. 3. Oral administration of each SSRI suppressed significantly the marble-burying behaviour with no change in locomotor activity in mice, and the extent and time course of suppression agreed well with those of brain SERT binding. Thus, the pharmacological potencies of SSRIs in the attenuation of marble-burying behaviour correlated significantly with their brain SERT binding activities. 4. In conclusion, the present study has provided the first in vivo evidences to support that fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, paroxetine and sertraline orally administered bind to the pharmacologically relevant brain SERT in mice and that their SERT-binding characteristics is closely associated with the pharmacokinetics and inhibition of marble-burying behaviour.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo identification and characterization of binding sites for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in mouse brain.Life Sci. 2004 Oct 29;75(24):2933-45. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.05.030. Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15454344
-
Pharmacokinetics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Jan;85(1):11-28. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(99)00048-0. Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 10674711 Review.
-
Effects of continuous administration of paroxetine on ligand binding site and expression of serotonin transporter protein in mouse brain.Brain Res. 2005 Aug 16;1053(1-2):154-61. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.06.038. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16051196
-
Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments on serotonin transporter function, density, and mRNA level.J Neurosci. 1999 Dec 1;19(23):10494-501. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-23-10494.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10575045 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996 Dec;31(6):444-69. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199631060-00004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996. PMID: 8968657 Review.
Cited by
-
Antidepressant Sertraline Is a Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Enteroviruses Targeting Viral Entry through Neutralization of Endolysosomal Acidification.Viruses. 2022 Jan 8;14(1):109. doi: 10.3390/v14010109. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35062313 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mood stabilizers on marble-burying behavior in mice: involvement of GABAergic system.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Mar;226(2):295-305. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2904-9. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23086022
-
Neurochemical responses to antidepressants in the prefrontal cortex of mice and their efficacy in preclinical models of anxiety-like and depression-like behavior: a comparative and correlational study.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 May;197(4):567-80. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1070-6. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18274731
-
Comparative effects of sertraline, haloperidol or olanzapine treatments on ketamine-induced changes in mouse behaviours.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Oct;32(5):1475-1489. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0031-3. Epub 2017 May 15. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 28508340
-
Flow cytometric analysis of BrdU incorporation as a high-throughput method for measuring adult neurogenesis in the mouse.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2009 Mar-Apr;59(2):100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2008.12.002. Epub 2008 Dec 14. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2009. PMID: 19121403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BOSKER F.J., KLOMPMAKERS A.A., WESTENBERG H.G. Effects of single and repeated oral administration of fluvoxamine on extracellular serotonin in the median raphe nucleus and dorsal hippocampus of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34:501–508. - PubMed
-
- CACCIA S., CAPPI M., FRACASSO C., GARATTINI S. Influence of dose and route of administration on the kinetics of fluoxetine and its metabolite norfluoxetine in the rat. Psychopharmacology. 1990;100:509–514. - PubMed
-
- FIGGITT D.P., MCCLELLAN K.J. Fluvoxamine. An updated review of its use in the management of adults with anxiety disorders. Drugs. 2000;60:925–954. - PubMed
-
- FULLER R.W., SNODDY H.D. Drug concentrations in mouse brain at pharmacologically active doses of fluoxetine enantiomers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993;45:2355–2358. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

