Andrographolide interferes with binding of nuclear factor-kappaB to DNA in HL-60-derived neutrophilic cells
- PMID: 15678086
- PMCID: PMC1576048
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706105
Andrographolide interferes with binding of nuclear factor-kappaB to DNA in HL-60-derived neutrophilic cells
Abstract
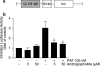
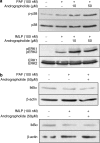
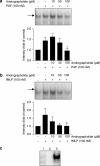
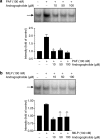
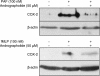
1. Andrographolide, the major active component from Andrographis paniculata, has shown to possess anti-inflammatory activity. Andrographolide inhibits the expression of several proinflammatory proteins that exhibit a nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) binding site in their gene. 2. In the present study, we analyzed the effect of andrographolide on the activation of NF-kappaB induced by platelet-activating factor (PAF) and N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) in HL-60 cells differentiated to neutrophils. 3. PAF (100 nM) and fMLP (100 nM) induced activation of NF-kappaB as determined by degradation of inhibitory factor B alpha (IkappaB alpha) using Western blotting in cytosolic extracts and by binding to DNA using electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) in nuclear extracts. 4. Andrographolide (5 and 50 microM) inhibited the NF-kappaB-luciferase activity induced by PAF. However, andrographolide did not reduce phosphorylation of p38 MAPK or ERK1/2 and did not change IkappaB alpha degradation induced by PAF and fMLP. 5. Andrographolide reduced the DNA binding of NF-kappaB in whole cells and in nuclear extracts induced by PAF and fMLP. 6. Andrographolide reduced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression induced by PAF and fMLP in HL-60/neutrophils. 7. It is concluded that andrographolide exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NF-kappaB binding to DNA, and thus reducing the expression of proinflammatory proteins, such as COX-2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Andrographolide acts as an anti-inflammatory agent in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by inhibiting STAT3-mediated suppression of the NF-κB pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jun 1;135(3):678-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.03.068. Epub 2011 Apr 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21497192
-
Thermal injury-induced priming effect of neutrophil is TNF-alpha and P38 dependent.Shock. 2006 Jul;26(1):69-76. doi: 10.1097/01.shk0000209531.38188.18. Shock. 2006. PMID: 16783201
-
Inhibitory effect of luteolin on TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 production in human colon epithelial cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2005 Jan;5(1):209-17. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.09.027. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15589482
-
Multi-Targeting Andrographolide, a Novel NF-κB Inhibitor, as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Stroke.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 27;18(8):1638. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081638. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28749412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a future for andrographolide to be an anti-inflammatory drug? Deciphering its major mechanisms of action.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 1;139:71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.03.024. Epub 2017 Apr 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28377280 Review.
Cited by
-
Andrographis paniculata decreases fatigue in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 12-month double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study.BMC Neurol. 2016 May 23;16:77. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0595-2. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27215274 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Andrographolide: A Herbal-Chemosynthetic Approach for Enhancing Immunity, Combating Viral Infections, and Its Implication on Human Health.Molecules. 2021 Nov 21;26(22):7036. doi: 10.3390/molecules26227036. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34834128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel role of andrographolide, an NF-kappa B inhibitor, on inhibition of platelet activation: the pivotal mechanisms of endothelial nitric oxide synthase/cyclic GMP.J Mol Med (Berl). 2011 Dec;89(12):1261-73. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0800-0. Epub 2011 Aug 6. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21822619
-
Andrographolide Ameliorates Inflammatory Changes Induced by D-Lactate in Bovine Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes.Animals (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;14(6):936. doi: 10.3390/ani14060936. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540033 Free PMC article.
-
Andrographolide: a new plant-derived antineoplastic entity on horizon.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:815390. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep135. Epub 2011 Feb 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 19752167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALI S., MANN D.A. Signal transduction via the NF-kappaB pathway: a targeted treatment modality for infection, inflammation and repair. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2004;22:67–79. - PubMed
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., BALTIMORE D. NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., HENKEL T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- BALDWIN A.S., JR The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- BARNES P.J., KARIN M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

