Effects of connexin-mimetic peptides on gap junction functionality and connexin expression in cultured vascular cells
- PMID: 15678088
- PMCID: PMC1576046
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706102
Effects of connexin-mimetic peptides on gap junction functionality and connexin expression in cultured vascular cells
Abstract
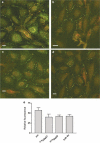
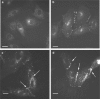
1. We have investigated the effects of connexin-mimetic peptides homologous to the Gap 26 and Gap 27 domains of Cxs 37, 40 and 43 against gap junctional communication and connexin expression in rat aortic endothelial cells (RAECs) and A7r5 myocytes. 2. Immunostaining and Western blot analysis confirmed the presence of gap junction plaques containing Cx43, but not Cx40, in RAECs, whereas plaques containing Cxs 40 and 43 were evident in A7r5 cells. Expression of Cx37 was limited in RAECs and absent from A7r5 cells. 3. Under control conditions calcein-loaded RAECs transferred dye to approximately 70% of subjacent A7r5 cells after coculture for 4-5 h. Dye transfer was inhibited by a peptide targeted to Cxs 37 and 43 ((37,43)Gap 27), but minimally affected by peptides targeted to Cxs 37 and 40 ((37,40)Gap 26 and (40)Gap 27). These findings suggest that the myoendothelial gap junctions that couple RAECs and A7r5 cells are constructed principally from Cx43. 4. Inhibition of dye transfer from RAECs to A7r5 cells cocultured in the presence of (37,43)Gap 27 plus (37,40)Gap 26 for 5 h was fully reversible. 5. In A7r5 cells, endogenous expression of Cx40 and Cx43 was unaffected by incubation with (37,43)Gap 27, (37,40)Gap 26, either individually or in combination, and the peptide combination did not impair connexin trafficking or the de novo formation of gap plaques in A7r5 cells transfected to express Cx43-GFP. 6. Treatment of A7r5 cells with (37,43)Gap 27 plus (37,40)Gap 26 abolished synchronized oscillations in intracellular [Ca2+] induced by the alpha1-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine. 7. The reversibility and lack of effect of the peptides on plaque formation suggests that they may be considered ideal probes for functional studies of connexin-mediated communication in the vascular wall.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NO, via its target Cx37, modulates calcium signal propagation selectively at myoendothelial gap junctions.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 May 15;12:33. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-33. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 24885166 Free PMC article.
-
Ouabain exerts biphasic effects on connexin functionality and expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;140(7):1261-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705556. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. Corrected and republished in: Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;141(2):374-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705671. PMID: 14645140 Free PMC article. Corrected and republished.
-
Oxidized phospholipids alter vascular connexin expression, phosphorylation, and heterocellular communication.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Oct;26(10):2216-21. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000237608.19055.53. Epub 2006 Jul 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16857951
-
Vascular gap junctions and implications for hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004 Oct;31(10):659-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2004.04071.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15554905 Review.
-
Molecular regulation of myoendothelial gap junctions.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;45:16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30999095 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Endothelial Connexin37 Reduces Angiogenesis and Decreases Tumor Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 8;23(6):2930. doi: 10.3390/ijms23062930. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328350 Free PMC article.
-
Ca²⁺-dependent nitric oxide release in the injured endothelium of excised rat aorta: a promising mechanism applying in vascular prosthetic devices in aging patients.BMC Surg. 2013;13 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2482-13-S2-S40. Epub 2013 Oct 8. BMC Surg. 2013. PMID: 24266895 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of connexin-mimetic peptides on perfusion pressure in response to phenylephrine in isolated, perfused rat kidneys.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011 Apr;15(2):203-11. doi: 10.1007/s10157-010-0382-0. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21153751
-
Connexins in Cardiovascular and Neurovascular Health and Disease: Pharmacological Implications.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Oct;69(4):396-478. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.012062. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28931622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gap Junction Channels of Innexins and Connexins: Relations and Computational Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 19;20(10):2476. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102476. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31109150 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BERMAN R.S., MARTIN P.E., EVANS W.H., GRIFFITH T.M. Relative contributions of NO and gap junctional communication to endothelium-dependent relaxations of rabbit resistance arteries vary with vessel size. Microvasc. Res. 2002;63:115–128. - PubMed
-
- BOITANO S., EVANS W.H. Connexin mimetic peptides reversibly inhibit Ca2+ signaling through gap junctions in airway cells. Am. J. Physiol. 2000;279:L623–L630. - PubMed
-
- BRAET K., VANDAMME W., MARTIN P.E., EVANS W.H., LEYBAERT L. Photoliberating inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate triggers ATP release that is blocked by the connexin-mimetic peptide gap 26. Cell Calcium. 2003;33:37–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

