The profile of repeat-associated histone lysine methylation states in the mouse epigenome
- PMID: 15678104
- PMCID: PMC549616
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600545
The profile of repeat-associated histone lysine methylation states in the mouse epigenome
Abstract
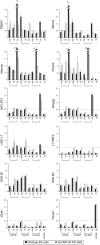
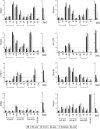
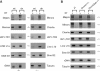
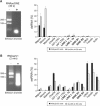
Histone lysine methylation has been shown to index silenced chromatin regions at, for example, pericentric heterochromatin or of the inactive X chromosome. Here, we examined the distribution of repressive histone lysine methylation states over the entire family of DNA repeats in the mouse genome. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation in a cluster analysis representing repetitive elements, our data demonstrate the selective enrichment of distinct H3-K9, H3-K27 and H4-K20 methylation marks across tandem repeats (e.g. major and minor satellites), DNA transposons, retrotransposons, long interspersed nucleotide elements and short interspersed nucleotide elements. Tandem repeats, but not the other repetitive elements, give rise to double-stranded (ds) RNAs that are further elevated in embryonic stem (ES) cells lacking the H3-K9-specific Suv39h histone methyltransferases. Importantly, although H3-K9 tri- and H4-K20 trimethylation appear stable at the satellite repeats, many of the other repeat-associated repressive marks vary in chromatin of differentiated ES cells or of embryonic trophoblasts and fibroblasts. Our data define a profile of repressive histone lysine methylation states for the repetitive complement of four distinct mouse epigenomes and suggest tandem repeats and dsRNA as primary triggers for more stable chromatin imprints.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suv39h-mediated histone H3 lysine 9 methylation directs DNA methylation to major satellite repeats at pericentric heterochromatin.Curr Biol. 2003 Jul 15;13(14):1192-200. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00432-9. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12867029
-
Histone lysine trimethylation exhibits a distinct perinuclear distribution in Plzf-expressing spermatogonia.Dev Biol. 2006 May 15;293(2):461-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.02.013. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16549060
-
Distinct dynamics and distribution of histone methyl-lysine derivatives in mouse development.Dev Biol. 2004 Dec 15;276(2):337-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.08.038. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15581869
-
Chromatin-based silencing mechanisms.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004 Oct;7(5):521-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.07.003. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004. PMID: 15337094 Review.
-
The indexing potential of histone lysine methylation.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:22-37; discussion 37-47, 163-9. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15171245 Review.
Cited by
-
Allele-specific programming of Npy and epigenetic effects of physical activity in a genetic model of depression.Transl Psychiatry. 2013 May 7;3(5):e255. doi: 10.1038/tp.2013.31. Transl Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23652932 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence deeper without sequencing more: Bayesian resolution of ambiguously mapped reads.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Apr 19;17(4):e1008926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008926. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33872311 Free PMC article.
-
BGDB: a database of bivalent genes.Database (Oxford). 2013 Jul 26;2013:bat057. doi: 10.1093/database/bat057. Print 2013. Database (Oxford). 2013. PMID: 23894186 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing differently affects protein-coding genes in D. melanogaster and H. sapiens.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 14;5:11550. doi: 10.1038/srep11550. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26169954 Free PMC article.
-
The transposon-driven evolutionary origin and basis of histone deacetylase functions and limitations in disease prevention.Clin Epigenetics. 2011 Aug;2(2):97-112. doi: 10.1007/s13148-011-0020-z. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Clin Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 22704332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen TA, von Kaenel S, Goodrich JA, Kugel JF (2004) The SINE-encoded mouse B2 RNA represses mRNA transcription in response to heat shock. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 816–821 - PubMed
-
- Bourc'his D, Bestor TH (2004) Meiotic catastrophe and retrotransposon reactivation in male germ cells lacking Dnmt3L. Nature 431: 96–99 - PubMed
-
- Cawley S, Bekiranov S, Ng HH, Kapranov P, Sekinger EA, Kampa D, Piccolboni A, Sementchenko V, Cheng J, Williams AJ, Wheeler R, Wong B, Drenkow J, Yamanaka M, Patel S, Brubaker S, Tammana H, Helt G, Struhl K, Gingeras TR (2004) Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of non-coding RNAs. Cell 116: 499–509 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

