Gap-junction channels inhibit transverse propagation in cardiac muscle
- PMID: 15679888
- PMCID: PMC549032
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-925X-4-7
Gap-junction channels inhibit transverse propagation in cardiac muscle
Abstract
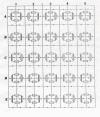
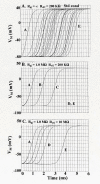
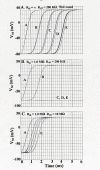
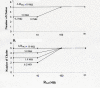
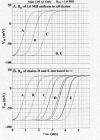
The effect of adding many gap-junctions (g-j) channels between contiguous cells in a linear chain on transverse propagation between parallel chains was examined in a 5 x 5 model (5 parallel chains of 5 cells each) for cardiac muscle. The action potential upstrokes were simulated using the PSpice program for circuit analysis. Either a single cell was stimulated (cell A1) or the entire chain was stimulated simultaneously (A-chain). Transverse velocity was calculated from the total propagation time (TPT) from when the first AP crossed a Vm of -20 mV and the last AP crossed -20 mV. The number of g-j channels per junction was varied from zero to 100, 1,000 and 10,000 (Rgj of infinity, 100 MOmega, 10 MOmega, 1.0 MOmega, respectively). The longitudinal resistance of the interstitial fluid (ISF) space between the parallel chains (Rol2) was varied between 200 KOmega (standard value) and 1.0, 5.0, and 10 MOmega. The higher the Rol2 value, the tighter the packing of the chains. It was found that adding many g-j channels inhibited transverse propagation by blocking activation of all 5 chains, unless Rol2 was greatly increased above the standard value of 200 KOmega. This was true for either method of stimulation. This was explained by, when there is strong longitudinal coupling between all 5 cells of a chain awaiting excitation, there must be more transfer energy (i.e., more current) to simultaneously excite all 5 cells of a chain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transverse propagation in an expanded PSpice model for cardiac muscle with gap-junction ion channels.Biomed Eng Online. 2006 Jul 28;5:46. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-5-46. Biomed Eng Online. 2006. PMID: 16875501 Free PMC article.
-
Propagation of action potentials between parallel chains of cardiac muscle cells in PSpice simulation.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003 Jan;81(1):48-58. doi: 10.1139/y03-019. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12665257
-
Transverse propagation of action potentials between parallel chains of cardiac muscle and smooth muscle cells in PSpice simulations.Biomed Eng Online. 2004 Mar 3;3:5. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-3-5. Biomed Eng Online. 2004. PMID: 14998434 Free PMC article.
-
Role of gap junctions in the propagation of the cardiac action potential.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 May 1;62(2):309-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.035. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15094351 Review.
-
[Connexins and junctional channels. Roles in the spreading of cardiac electrical excitation and heart development].Pathol Biol (Paris). 2008 Jul;56(5):334-41. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2008.05.009. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18586407 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Transverse propagation in an expanded PSpice model for cardiac muscle with gap-junction ion channels.Biomed Eng Online. 2006 Jul 28;5:46. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-5-46. Biomed Eng Online. 2006. PMID: 16875501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Picone JB, Sperelakis N, Mann JE., Jr Expanded model of the electric field Hypothesis for propagation in cardiac muscle. Math and computer modeling. 1991;15:17–35. doi: 10.1016/0895-7177(91)90079-M. - DOI
-
- Sperelakis N, McConnell K. An electric field mechanism for transmission of excitation from cell to cell in cardiac muscle and smooth muscles. In: Mohan RM, editor. Research Advances in Biomedical Engineering. Vol. 2. Global Research Network; 2001. pp. 39–66.
-
- Pertsov AM, Medvinski AB. Electric coupling in cells without highly permeable cell contacts. Biofizika. 1976;21:698–700. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

