Inhibition of Beta interferon induction by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus suggests a two-step model for activation of interferon regulatory factor 3
- PMID: 15681410
- PMCID: PMC546554
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.4.2079-2086.2005
Inhibition of Beta interferon induction by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus suggests a two-step model for activation of interferon regulatory factor 3
Abstract
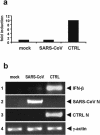
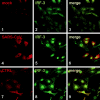
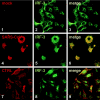
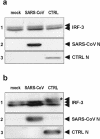
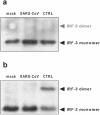
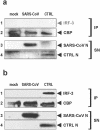
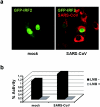
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a novel coronavirus termed SARS-CoV. We and others have previously shown that the replication of SARS-CoV can be suppressed by exogenously added interferon (IFN), a cytokine which is normally synthesized by cells as a reaction to virus infection. Here, we demonstrate that SARS-CoV escapes IFN-mediated growth inhibition by preventing the induction of IFN-beta. In SARS-CoV-infected cells, no endogenous IFN-beta transcripts and no IFN-beta promoter activity were detected. Nevertheless, the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3), which is essential for IFN-beta promoter activity, was transported from the cytoplasm to the nucleus early after infection with SARS-CoV. However, at a later time point in infection, IRF-3 was again localized in the cytoplasm. By contrast, IRF-3 remained in the nucleus of cells infected with the IFN-inducing control virus Bunyamwera delNSs. Other signs of IRF-3 activation such as hyperphosphorylation, homodimer formation, and recruitment of the coactivator CREB-binding protein (CBP) were found late after infection with the control virus but not with SARS-CoV. Our data suggest that nuclear transport of IRF-3 is an immediate-early reaction to virus infection and may precede its hyperphosphorylation, homodimer formation, and binding to CBP. In order to escape activation of the IFN system, SARS-CoV appears to block a step after the early nuclear transport of IRF-3.
Figures
References
-
- Basler, C. F., and A. Garcia-Sastre. 2002. Viruses and the type I interferon antiviral system: induction and evasion. Int. Rev. Immunol. 21:305-337. - PubMed
-
- Baudoux, P., L. Besnardeau, C. Carrat, P. Rottier, B. Charley, and H. Laude. 1998. Interferon alpha inducing property of coronavirus particles and pseudoparticles. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 440:377-386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

