Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 5 are overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and contribute to extracellular matrix deposition
- PMID: 15681824
- PMCID: PMC1602317
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62263-8
Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 5 are overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and contribute to extracellular matrix deposition
Abstract
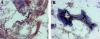
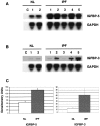
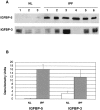
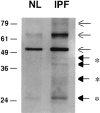
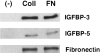
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fibrotic disease of unknown etiology that results in significant morbidity and mortality. The pathogenesis of IPF is not completely understood. Because recent studies have implicated insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in the pathogenesis of fibrosis, we examined the expression and function of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP)-3 and -5 in IPF. IGFBP-3 and -5 levels were increased in vivo in IPF lung tissues and in vitro in fibroblasts cultured from IPF lung. The IGFBPs secreted by IPF fibroblasts are functionally active and can bind IGF-I, and IGFBPs secreted by primary fibroblasts bind extracellular matrix components. Our results also suggest that IGFBPs may be involved in the initiation and/or perpetuation of fibrosis by virtue of their ability to induce the production of extracellular matrix components such as collagen type I and fibronectin in normal primary adult lung fibroblasts. Although transforming growth factor-beta increased IGFBP-3 production by primary fibroblasts in a time-dependent manner, IGFBP-5 levels were not increased by transforming growth factor-beta. Taken together, our results suggest that IGFBPs play an important role in the development of fibrosis in IPF.
Figures

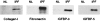



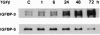
References
-
- King TE, Jr, Tooze JA, Schwarz MI, Brown KR, Cherniack RM. Predicting survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1171–1181. - PubMed
-
- King TE, Jr, Schwarz MI, Brown K, Tooze JA, Colby TV, Waldron JA, Jr, Flint A, Thurlbeck W, Cherniack RM. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Relationship between histopathologic features and mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1025–1032. - PubMed
-
- Selman M, King T, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med 2001. 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed
-
- Ward A, Hunninghake GW. Lung Inflammation and fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:S123–S129. - PubMed
-
- Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocrine Rev. 1995;16:3–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

