A case of severe protein-losing enteropathy as a late complication of pelvic irradiation
- PMID: 15683118
- PMCID: PMC4531575
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2004.19.4.271
A case of severe protein-losing enteropathy as a late complication of pelvic irradiation
Abstract
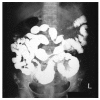
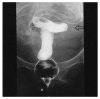
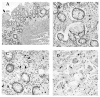
Protein-losing enteropathy is the manifestation of a diverse set of disorders, and it is characterized by the excessive loss of plasma proteins into the affected portions of the gastrointestinal tract, and this results in hypoalbuminemia. We report here on a case of severe protein-losing enteropathy with the typical clinical features of hypoalbuminemia, dependent edema and increased alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha1-AT) clearance, as measured by using 24 hr stool testing. The associated disorder with the protein-losing enteropathy of our case was radiation enterocolitis and lymphatic obstruction that was due to radiation treatment and lymph node dissection in the remote past for the treatment of uterine cervical carcinoma. Our case suggests that chronic radiation enterocolitis can result in irreversible injury to the intestinal mucosa and a protein-losing enteropathy, which can bring about a very poor quality of life and even the loss of life.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Protein-losing enteropathy].Rev Med Interne. 2015 Jul;36(7):467-73. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2014.12.001. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Rev Med Interne. 2015. PMID: 25618488 Review. French.
-
Lupus-associated protein-losing enteropathy.Arch Intern Med. 1990 Sep;150(9):1806-10. Arch Intern Med. 1990. PMID: 2203319 Review.
-
Protein-losing enteropathy associated with egg allergy in a 5-month-old boy.J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2008;18(1):63-6. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18361105
-
[Edema and protein-losing enteropathy complicating chronic constrictive pericarditis associated with an ascending aortic aneurysm].Presse Med. 2008 Jan;37(1 Pt 1):55-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2007.05.027. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Presse Med. 2008. PMID: 17988828 French.
-
[Protein-losing enteropathy and cerebral infarction associated with systemic lupus erythematosus].Ryumachi. 1994 Feb;34(1):59-63. Ryumachi. 1994. PMID: 8146730 Japanese.
References
-
- Kim KE. Protein-losing gastroenteropathy. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleigenger MH, editors. Sleigenger & Fordtran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease. 7th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2002. pp. 446–452.
-
- Goldberg RI, Calleja GA. Protein-losing gastroenteropathy. In: Haubrich WS, Schaffner F, Berk J, editors. Bockus gastroenterology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1995. pp. 1072–1086.
-
- Magazzu G, Jacono G, di Pasquale G, Sferlazzas C, Tedeschi A, Santoro S, Nibali SC, Musso F, Balsamo V. Reliability and usefulness of random fecal alpha 1-antitrypsin concentration: further simplification of the method. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985;4:402–407. - PubMed
-
- Hill RE, Hercz A, Corey ML, Gilday DL, Hamilton JR. Fecal clearance of alpha 1-antitrypsin: a reliable measure of enteric protein loss in children. J Pediatr. 1981;99:416–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
