The sustainability of interactions between the orexin-1 receptor and beta-arrestin-2 is defined by a single C-terminal cluster of hydroxy amino acids and modulates the kinetics of ERK MAPK regulation
- PMID: 15683363
- PMCID: PMC1134986
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041745
The sustainability of interactions between the orexin-1 receptor and beta-arrestin-2 is defined by a single C-terminal cluster of hydroxy amino acids and modulates the kinetics of ERK MAPK regulation
Abstract
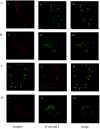
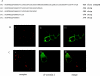
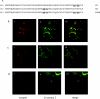
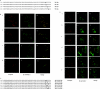
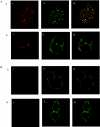
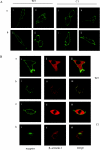
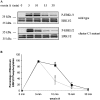
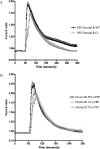
The orexin-1 receptor interacts with beta-arrestin-2 in an agonist-dependent manner. In HEK-293T cells, these two proteins became co-internalized into acidic endosomes. Truncations from the C-terminal tail did not prevent agonist-induced internalization of the orexin-1 receptor or alter the pathway of internalization, although such mutants failed to interact with beta-arrestin-2 in a sustained manner or produce its co-internalization. Mutation of a cluster of three threonine and one serine residue at the extreme C-terminus of the receptor greatly reduced interaction and abolished co-internalization of beta-arrestin-2-GFP (green fluorescent protein). Despite the weak interactions of this C-terminally mutated form of the receptor with beta-arrestin-2, studies in wild-type and beta-arrestin-deficient mouse embryo fibroblasts confirmed that agonist-induced internalization of this mutant required expression of a beta-arrestin. Although without effect on agonist-mediated elevation of intracellular Ca2+ levels, the C-terminally mutated form of the orexin-1 receptor was unable to sustain phosphorylation of the MAPKs (mitogen-activated protein kinases) ERK1 and ERK2 (extracellular-signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2) to the same extent as the wild-type receptor. These studies indicate that a single cluster of hydroxy amino acids within the C-terminal seven amino acids of the orexin-1 receptor determine the sustainability of interaction with beta-arrestin-2, and indicate an important role of beta-arrestin scaffolding in defining the kinetics of orexin-1 receptor-mediated ERK MAPK activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A phosphorylation cluster of five serine and threonine residues in the C-terminus of the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor is important for desensitization but not for beta-arrestin-mediated ERK activation.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Nov;20(11):3014-26. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0098. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16887887
-
Visualizing differences in ligand-induced beta-arrestin-GFP interactions and trafficking between three recently characterized G protein-coupled receptors.J Neurochem. 2001 Apr;77(2):476-85. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00269.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11299310
-
Role of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase site serine cluster in beta2-adrenergic receptor internalization, desensitization, and beta-arrestin translocation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):7684-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500328200. Epub 2006 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407241
-
Stable interaction between beta-arrestin 2 and angiotensin type 1A receptor is required for beta-arrestin 2-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48255-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406205200. Epub 2004 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15355986
-
Scaffolding of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling by β-Arrestins.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 17;23(2):1000. doi: 10.3390/ijms23021000. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polarity protein Par3 controls B-cell receptor dynamics and antigen extraction at the immune synapse.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Apr 1;26(7):1273-85. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-09-1373. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25631815 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular network map of orexin-orexin receptor signaling system.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar;17(1):217-227. doi: 10.1007/s12079-022-00700-3. Epub 2022 Dec 8. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36480100 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin Signaling: A Complex, Multifaceted Process.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 13;16:812359. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.812359. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35496914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The exocyst controls lysosome secretion and antigen extraction at the immune synapse of B cells.J Cell Biol. 2019 Jul 1;218(7):2247-2264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201811131. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31197029 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal profiling of orexin receptor-arrestin-ubiquitin complexes reveals differences between receptor subtypes.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):16726-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.223537. Epub 2011 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21378163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakurai T., Amemiya A., Ishii M., Matsuzaki I., Chemelli R. M., Tanaka H., Williams S. C., Richardson J. A., Kozlowski G. P., Wilson S., et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–585. - PubMed
-
- Samson W. K., Resch Z. T. The hypocretin/orexin story. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000;11:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Smart D., Jerman J. C., Brough S. J., Rushton S. L., Murdock P. R., Jewitt F., Elshourbagy N. A., Ellis C. E., Middlemiss D. N., Brown F. Characterization of recombinant human orexin receptor pharmacology in a Chinese hamster ovary cell-line using FLIPR. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999;128:1–3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lund P. E., Shariatmadari R., Uustare A., Detheux M., Parmentier M., Kukkonen J. P., Akerman K. E. The orexin OX1 receptor activates a novel Ca2+ influx pathway necessary for coupling to phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:30806–30812. - PubMed
-
- Haynes A. C., Jackson B., Chapman H., Tadayyon M., Johns A., Porter R. A., Arch J. R. A selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist reduces food consumption in male and female rats. Regul. Pept. 2000;96:45–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

