E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of the trifunctional ARD1 (ADP-ribosylation factor domain protein 1)
- PMID: 15684077
- PMCID: PMC548593
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409800102
E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of the trifunctional ARD1 (ADP-ribosylation factor domain protein 1)
Abstract
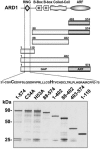
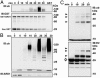
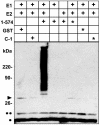
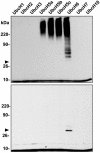
Protein ubiquitinylation plays a key role in many important cellular processes. Ubiquitinylation requires the E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme, an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, and, frequently, a substrate-specific E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. In one class of E3 ubiquitin ligases, the catalytic domain contains a zinc-binding RING finger motif. ARD1 (ADP-ribosylation factor domain protein 1), with a RING finger domain in the N-terminal region, two predicted B-Boxes, and a coiled-coil protein interaction motif immediately preceding an ADP-ribosylation factor domain at the C terminus, belongs to the TRIM (Tripartite motif) or RBCC (RING, B-Box, coiled-coil) family. The region containing the B-Boxes and the coiled-coil motif acts as a GTPase-activating protein for the ADP-ribosylation factor domain of ARD1. We report here that full-length ARD1 or the RING finger domain (residues 1-110) produced polyubiquitinylated proteins in vitro in the presence of mammalian E1, an E2 enzyme (UbcH6 or UbcH5a, -5b, or -5c), ATP, and ubiquitin. Deletion of the RING region or point mutations within the RING sequence abolished ARD1 E3 ligase activity. All data are consistent with a potential function for ARD1 as an E3 ubiquitin ligase in cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ADP-ribosylation factor domain protein 1 (ARD1), a multifunctional protein with ubiquitin E3 ligase, GAP, and ARF domains.Methods Enzymol. 2005;404:195-206. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)04019-X. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413270
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 and is isolated RING finger domain act as ubiquitin E3 ligases in vitro.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(2):841-50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.2.841-850.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11752173 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and catalytic activation of the TRIM23 RING E3 ubiquitin ligase.Proteins. 2017 Oct;85(10):1957-1961. doi: 10.1002/prot.25348. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Proteins. 2017. PMID: 28681414 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C: a potential cancer biomarker.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;47:113-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24361302 Review.
-
TRIM proteins as RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:27-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5398-7_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23630998 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and biophysical characterization of a chimeric TRIM21-TRIM5alpha protein.J Virol. 2008 Dec;82(23):11669-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01559-08. Epub 2008 Sep 17. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18799572 Free PMC article.
-
Midline2 is overexpressed and a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer and promotes breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo.Front Med. 2016 Mar;10(1):41-51. doi: 10.1007/s11684-016-0429-z. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Front Med. 2016. PMID: 26791755
-
A synopsis of eukaryotic Nalpha-terminal acetyltransferases: nomenclature, subunits and substrates.BMC Proc. 2009 Aug 4;3 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S2. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-3-S6-S2. BMC Proc. 2009. PMID: 19660095 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TRIM23 as a cofactor involved in the regulation of NF-kappaB by human cytomegalovirus.J Virol. 2009 Apr;83(8):3581-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02072-08. Epub 2009 Jan 28. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19176615 Free PMC article.
-
Grouper TRIM23 exerts antiviral activity against iridovirus and nodavirus.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:985291. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.985291. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36203610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moss, J. & Vaughan, M. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 21431–21434. - PubMed
-
- Moss, J. & Vaughan, M. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12327–12330. - PubMed
-
- Kahn, R. A. & Gilman, A. G. (1984) J. Biol. Chem. 259, 6228–6234. - PubMed
-
- Holthuis, J. C. & Burger, K. N. (2003) Dev. Cell 5, 821–822. - PubMed
-
- Nie, Z., Hirsch, D. S. & Randazzo, P. A. (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 396–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

