Serine racemase: activation by glutamate neurotransmission via glutamate receptor interacting protein and mediation of neuronal migration
- PMID: 15684087
- PMCID: PMC548584
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409723102
Serine racemase: activation by glutamate neurotransmission via glutamate receptor interacting protein and mediation of neuronal migration
Abstract
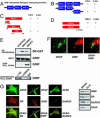
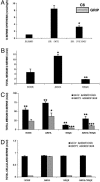
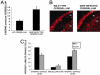
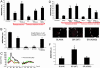
Serine racemase (SR), localized to astrocytic glia that ensheathe synapses, converts L-serine to D-serine, an endogenous ligand of the NMDA receptor. We report the activation of SR by glutamate neurotransmission involving alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors via glutamate receptor interacting protein (GRIP) and the physiologic regulation of cerebellar granule cell migration by SR. GRIP physiologically binds SR, augmenting SR activity and D-serine release. GRIP infection of neonatal mouse cerebellum in vivo enhances granule cell migration. Selective degradation of D-serine by D-amino acid oxidase and pharmacologic inhibition of SR impede migration, whereas D-serine activates the process. Thus, in neuronal migration, glutamate stimulates Bergmann glia to form and release D-serine, which, together with glutamate, activates NMDA receptors on granule neurons, chemokinetically enhancing migration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serine racemase regulated by binding to stargazin and PSD-95: potential N-methyl-D-aspartate-α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (NMDA-AMPA) glutamate neurotransmission cross-talk.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 24;289(43):29631-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.571604. Epub 2014 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25164819 Free PMC article.
-
Factors regulating serine racemase and d-amino acid oxidase expression in the mouse striatum.Brain Res. 2021 Jan 15;1751:147202. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147202. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33171153 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic regulation of serine racemase via reversal of PIP2 inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 24;106(8):2921-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813105106. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19193859 Free PMC article.
-
D-Serine as a glial modulator of nerve cells.Glia. 2004 Aug 15;47(3):275-283. doi: 10.1002/glia.20073. Glia. 2004. PMID: 15252817 Review.
-
[Endogenous D-serine in mammalian brains].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Feb;20(1):33-9. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 10890022 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Bergmann glia function in granule cell migration during cerebellum development.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Apr;47(2):833-44. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8405-y. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23329344 Review.
-
Control of cortical neuronal migration by glutamate and GABA.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jan 30;9:4. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00004. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25688185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic exposure of mutant DISC1 mice to lead produces sex-dependent abnormalities consistent with schizophrenia and related mental disorders: a gene-environment interaction study.Schizophr Bull. 2014 May;40(3):575-84. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbt071. Epub 2013 May 28. Schizophr Bull. 2014. PMID: 23716713 Free PMC article.
-
The role of astrocytes in depression, its prevention, and treatment by targeting astroglial gliotransmitter release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2307953121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2307953121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495924 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolytic flux controls D-serine synthesis through glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in astrocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):E2217-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1416117112. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25870284 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

