In psychosis, cortical interneurons overexpress DNA-methyltransferase 1
- PMID: 15684088
- PMCID: PMC548582
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409665102
In psychosis, cortical interneurons overexpress DNA-methyltransferase 1
Abstract
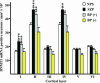
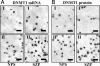
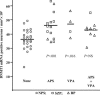
Cortical DNA-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) is preferentially expressed in interneurons secreting GABA where it very likely contributes to promoter CpG island hypermethylation, thus causing a down-regulation of promoter functions. To consolidate and expand on previous findings that, in the cortex of schizophrenia (SZ) brains, glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) expression is down-regulated whereas that of DNMT1 is up-regulated, we studied both parameters in Brodmann's area (BA) 9 from the McLean 66 Cohort Collection (Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center, Belmont, MA). In BA9 of SZ and bipolar disorder patients with psychosis, DNMT1 mRNA and protein expression preferentially increases in layer I, II, and IV interneurons, and this increase is paralleled by a decreased number of GAD67 mRNA-positive neurons. The increase in DNMT1 and the decrease in GAD67-expressing neurons were unrelated to postmortem interval, pH, RNA quality, or to the presence, dose, or duration of antipsychotic (APS) medication, with the exception of a subgroup of SZ patients treated with a combination of valproate and APS in which the expression of DNMT1 failed to change. The DNMT1 increase and the GAD67 decrease in BA9 interneurons are significant features of SZ and bipolar disorder with psychosis. Interestingly, the DNMT1 increase failed to occur when patients with psychosis received a combination of valproate and APS treatment but not APS monotherapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA-methyltransferase 1 mRNA is selectively overexpressed in telencephalic GABAergic interneurons of schizophrenia brains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):348-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2637013100. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14684836 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methyltransferase 1 regulates reelin mRNA expression in mouse primary cortical cultures.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 1;102(5):1749-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409648102. Epub 2005 Jan 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15671176 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methyltransferase inhibitors coordinately induce expression of the human reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 genes.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;71(3):644-53. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.030635. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17065238
-
The human reelin gene: transcription factors (+), repressors (-) and the methylation switch (+/-) in schizophrenia.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Jul;111(1):272-86. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.01.007. Epub 2006 Mar 30. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16574235 Review.
-
GABAergic cortical neuron chromatin as a putative target to treat schizophrenia vulnerability.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003;15(2):121-42. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v15.i2.20. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14977367 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered gene expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia.Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr;19(4):478-85. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.30. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23528911 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of TET1 and downregulation of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3C in the parietal cortex of psychotic patients.Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Sep 4;2(9):e159. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.86. Transl Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22948384 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics, behaviour, and health.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2008 Mar 15;4(1):37-49. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-4-1-37. Epub 2008 Mar 15. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 20525124 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd45 in Neuronal Development, Function, and Injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1360:117-148. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-94804-7_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35505167 Review.
-
GAD1 mRNA expression and DNA methylation in prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia.PLoS One. 2007 Aug 29;2(8):e809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000809. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17726539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petronis, A. (2004) Biol. Psychiatry 55, 965-970. - PubMed
-
- Costa, E., Chen, Y., Davis, J. M., Dong, E., Noh, J., S., Tremolizzo, L., Veldic, M., Grayson, D. R. & Guidotti, A. (2002) Mol. Interv. 2, 47-57. - PubMed
-
- Costa, E., Grayson, D. R., Mitchell, C. P., Tremolizzo, L., Veldic, M. & Guidotti, A. (2003) Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 15, 121-142. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian, S., Kim, J. J., Potkin, S. G., Hagman, J. O., Tafazzoli, A., Bunney, W. E., Jr., & Jones, E. G. (1995) Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 52, 258-266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

