A highly specific phosphatase that acts on ADP-ribose 1''-phosphate, a metabolite of tRNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 15684411
- PMCID: PMC548356
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki211
A highly specific phosphatase that acts on ADP-ribose 1''-phosphate, a metabolite of tRNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
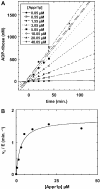
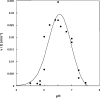
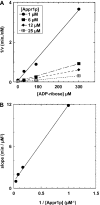
One molecule of ADP-ribose 1'',2''-cyclic phosphate (Appr>p) is formed during each of the approximately 500 000 tRNA splicing events per Saccharomyces cerevisiae generation. The metabolism of Appr>p remains poorly defined. A cyclic phosphodiesterase (Cpd1p) has been shown to convert Appr>p to ADP-ribose-1''-phosphate (Appr1p). We used a biochemical genomics approach to identify two yeast phosphatases that can convert Appr1p to ADP-ribose: the product of ORF YBR022w (now Poa1p), which is completely unrelated to other known phosphatases; and Hal2p, a known 3'-phosphatase of 5',3'-pAp. Poa1p is highly specific for Appr1p, and thus likely acts on this molecule in vivo. Poa1 has a relatively low K(M) for Appr1p (2.8 microM) and a modest kcat (1.7 min(-1)), but no detectable activity on several other substrates. Furthermore, Poa1p is strongly inhibited by ADP-ribose (K(I), 17 microM), modestly inhibited by other nucleotides containing an ADP-ribose moiety and not inhibited at all by other tested molecules. In contrast, Hal2p is much more active on pAp than on Appr1p, and several other tested molecules were Hal2p substrates or inhibitors. poa1-Delta mutants have no obvious growth defect at different temperatures in rich media, and analysis of yeast extracts suggests that approximately 90% of Appr1p processing activity originates from Poa1p.
Figures


References
-
- Peebles C.L., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Precise excision of intervening sequences from precursor tRNAs by a membrane-associated yeast endonuclease. Cell. 1983;32:525–536. - PubMed
-
- Trotta C.R., Miao F., Arn E.A., Stevens S.W., Ho C.K., Rauhut R., Abelson J.N. The yeast tRNA splicing endonuclease: a tetrameric enzyme with two active site subunits homologous to the archaeal tRNA endonucleases. Cell. 1997;89:849–858. - PubMed
-
- Phizicky E.M., Schwartz R.C., Abelson J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae tRNA ligase. Purification of the protein and isolation of the structural gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:2978–2986. - PubMed
-
- Phizicky E.M., Consaul S.A., Nehrke K.W., Abelson J. Yeast tRNA ligase mutants are nonviable and accumulate tRNA splicing intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:4577–4582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

