Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB
- PMID: 15685173
- PMCID: PMC1440292
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1166
Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB
Abstract
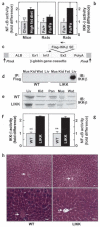
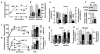
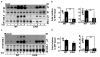
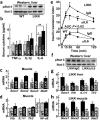
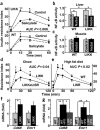
We show that NF-kappaB and transcriptional targets are activated in liver by obesity and high-fat diet (HFD). We have matched this state of chronic, subacute 'inflammation' by low-level activation of NF-kappaB in the liver of transgenic mice, designated LIKK, by selectively expressing constitutively active IKK-b in hepatocytes. These mice exhibit a type 2 diabetes phenotype, characterized by hyperglycemia, profound hepatic insulin resistance, and moderate systemic insulin resistance, including effects in muscle. The hepatic production of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha, was increased in LIKK mice to a similar extent as induced by HFD in in wild-type mice. Parallel increases were observed in cytokine signaling in liver and mucscle of LIKK mice. Insulin resistance was improved by systemic neutralization of IL-6 or salicylate inhibition of IKK-beta. Hepatic expression of the IkappaBalpha superrepressor (LISR) reversed the phenotype of both LIKK mice and wild-type mice fed an HFD. These findings indicate that lipid accumulation in the liver leads to subacute hepatic 'inflammation' through NF-kappaB activation and downstream cytokine production. This causes insulin resistance both locally in liver and systemically.
Figures
References
-
- Mokdad AH, et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289:76–79. - PubMed
-
- National Diabetes Data Group . Diabetes in America. 2nd National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive Diseases, National Institutes of Health; Bethesda, Maryland: 1995.
-
- Boden G, Shulman GI. Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2002;32(Suppl 3):14–23. - PubMed
-
- Seppala-Lindroos A, et al. Fat accumulation in the liver is associated with defects in insulin suppression of glucose production and serum free fatty acids independent of obesity in normal men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;87:3023–3028. - PubMed
-
- Ryysy L, et al. Hepatic fat content and insulin action on free fatty acids and glucose metabolism rather than insulin absorption are associated with insulin requirements during insulin therapy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2000;49:749–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

