Neurogenic double-peaked vasoconstriction of human gastroepiploic artery is mediated by both alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors
- PMID: 15685216
- PMCID: PMC1576054
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705975
Neurogenic double-peaked vasoconstriction of human gastroepiploic artery is mediated by both alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors
Abstract
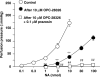
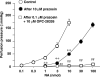
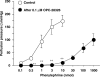
1. The contribution of postjunctional P2X receptors and subtypes of alpha-adrenoceptors to vasoconstrictor responses following periarterial electrical nerve stimulation (PNS, 30 s trains of pulses at a frequency of 2, 4 or 8 Hz) was investigated in human gastroepiploic arteries. 2. The vasoconstrictor response to PNS at a stimulation of 4 or 8 Hz was a two-peaked response, whereas at a frequency of 2 Hz it appeared only as a late peak. All vasoconstrictions evoked by PNS were abolished by phentolamine, a nonselective alpha-adrenoceptor inhibitor, but not by alpha,beta-methylene ATP, a P2X receptor-desensitizing agent. 3. The early peak to PNS at 4 or 8 Hz was abolished by prazosin, an alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonist, while the late one still remained, although it was markedly inhibited. The responses remaining after prazosin were blocked by rauwolscine. The vasoconstrictor response to PNS at 2 Hz was not affected by prazosin (0.1 microM), but was abolished by rauwolscine (0.1 microM), an alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonist. 4. OPC-28326 (10 microM), a newly developed vasodilator, which preferentially exerts its antagonistic actions on the alpha2B- and alpha2C-adrenoceptors, significantly reduced the noradrenaline-induced vasoconstriction in the absence or presence of prazosin. OPC-28326 had a greater inhibitory effect on the late peak evoked by PNS than the early one. The neurogenic responses remaining after OPC-28326 were abolished by prazosin. 5. The present results suggest that sympathetic vasoconstriction of the human gastroepiploic artery is mediated by both alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors postjunctionally, but not by P2X receptors. The alpha2-adrenoceptors may be preferentially activated at a low frequency of stimulation, which induces a constriction more slowly than that by alpha1-adrenoceptors. The existence of alpha2-adrenoceptors may cause an enhancement of alpha1-adrenoceptor-induced responses.
Figures

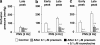
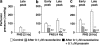

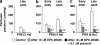
Similar articles
-
Purinergic and adrenergic cotransmission in canine isolated and perfused gastroepiploic arteries.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2003 Sep;30(9):678-83. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2003.03897.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12940888
-
Effects of a selective neuropeptide Y Y(1) receptor antagonist BIBP 3226 on double peaked vasoconstrictor responses to periarterial nerve stimulation in canine splenic arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(7):1699-705. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703484. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10928977 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenergic-purinergic interactions on vasoconstrictor responses to periarterial electric nerve stimulation in canine splenic arteries.J Auton Pharmacol. 1999 Jun;19(3):139-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2680.1999.00126.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10511469
-
[NPY as a periarterial sympathetic transmitter in isolated vessel].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Mar;117(3):187-94. doi: 10.1254/fpj.117.187. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11288488 Review. Japanese.
-
[ATP as a periarterial sympathetic transmitter in isolated vessel].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Aug;116(2):85-92. doi: 10.1254/fpj.116.85. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 10976460 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Acute dilation to alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonists uncovers dual constriction and dilation mediated by arterial alpha(2)-adrenoceptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;158(5):1344-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00403.x. Epub 2009 Sep 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19785657 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between alpha(1)- and alpha(2)-adrenoreceptors contributes to enhanced constrictor effects of norepinephrine in mesenteric veins compared to arteries.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 25;643(2-3):239-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.06.021. Epub 2010 Jun 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BAO J.-X., ERIKSSON I.E., STJÄRNE L. Neurogenic contractions in tail artery of normotensive rats are mediated by noradrenaline and ATP via postjunctional α1- and α2-adrenoceptors and P2X-purinoceptors. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1989;136:139–140. - PubMed
-
- BAO J.-X., GONON F., STJÄRNE L. Frequency- and train length-dependent variation in the roles of postjunctional α1- and α2-adrenoceptors for the field stimulation-induced neurogenic contraction of rat tail artery. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1993;347:601–616. - PubMed
-
- CHIBA S., YANG X.-P. Mechanisms of release of ATP from vascular purinergic nerves. Auton. Autacoid Pharmacol. 2003;23:95–104. - PubMed
-
- DOCHERTY J.R. Subtypes of functional α1- and α2-adrenoceptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998;361:1–15. - PubMed
-
- DÓDA M. Role of different subtypes of adrenoceptors in pressor responses to catecholamines released from sympathetic nerve endings. Brain Res. Bull. 1997;42:51–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

