Mutations in the amino-terminal domain of lambda-integrase have differential effects on integrative and excisive recombination
- PMID: 15686557
- PMCID: PMC1808434
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04447.x
Mutations in the amino-terminal domain of lambda-integrase have differential effects on integrative and excisive recombination
Abstract
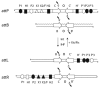
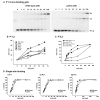
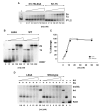
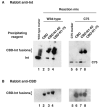
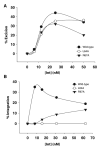
Lambda integrase (Int) forms higher-order protein-DNA complexes necessary for site-specific recombination. The carboxy-terminal domain of Int (75-356) is responsible for catalysis at specific core-type binding sites whereas the amino-terminal domain (1-70) is responsible for cooperative arm-type DNA binding. Alanine scanning mutagenesis of residues 64-70, within full-length integrase, has revealed differential effects on cooperative arm binding interactions that are required for integrative and excisive recombination. Interestingly, while these residues are required for cooperative arm-type binding on both P'1,2 and P'2,3 substrates, cooperative binding at the arm-type sites P'2,3 was more severely compromised than binding at arm-type sites P'1,2 for L64A. Concomitantly, L64A had a much stronger effect on integrative than on excisive recombination. The arm-binding properties of Int appear to be intrinsic to the amino-terminal domain because the phenotype of L64A was the same in an amino-terminal fragment (Int 1-75) as it was in the full-length protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of the effects of single-base and triple-base changes in the integrase arm-type binding sites on the site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda.Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3953-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3953. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990. PMID: 2142765 Free PMC article.
-
Differential affinity and cooperativity functions of the amino-terminal 70 residues of lambda integrase.J Mol Biol. 2002 Dec 6;324(4):775-89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01199-3. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12460577
-
Mutational analysis of protein binding sites involved in formation of the bacteriophage lambda attL complex.J Bacteriol. 1997 Feb;179(4):1059-67. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.4.1059-1067.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9023184 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the λ Integrase bridges in the nucleoprotein Holliday junction intermediates of viral integrative and excisive recombination.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Aug 26;111(34):12366-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1413007111. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25114247 Free PMC article.
-
The λ Integrase Site-specific Recombination Pathway.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0051-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0051-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tight regulation of the intS gene of the KplE1 prophage: a new paradigm for integrase gene regulation.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 7;6(10):e1001149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001149. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20949106 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific recombination systems in filamentous phages.Mol Genet Genomics. 2012 Jul;287(7):525-30. doi: 10.1007/s00438-012-0700-1. Epub 2012 Jun 3. Mol Genet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22661259 Review.
-
Architecture of the 99 bp DNA-six-protein regulatory complex of the lambda att site.Mol Cell. 2006 Nov 17;24(4):569-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.10.006. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 17114059 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of bacteriophage lambda integrases with altered recombination specificity by in vitro compartmentalization.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Mar;38(4):e25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1089. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19966270 Free PMC article.
-
The Integration and Excision of CTnDOT.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0020-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0020-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104696 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bauer CE, Hesse SD, Gumport RI, Gardner JF. Mutational analysis of integrase arm-type binding sites of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1986;192:513–527. - PubMed
-
- Campbell AM. Episomes. In: Caspari EW, Thoday JM, editors. Advances in Genetics. New York: Academic Press; 1962. pp. 101–145.
-
- Cheng Q, Swalla BM, Beck M, Alcaraz R, Jr, Gumport RI, Gardner JF. Specificity determinants for bacteriophage Hong Kong 022 integrase: analysis of mutants with relaxed core-binding specificities. Mol Microbiol. 2000;36:424–436. - PubMed
-
- Enquist L, Weisberg R. Flexibility in attachment site recognition by λ integrase. In: Bukhari A, Shaprio J, Adhya S, editors. DNA Insertion Elements, Plasmids and Episomes. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 1977. pp. 343–348.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

