A polysaccharide deacetylase homologue, PdaA, in Bacillus subtilis acts as an N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase in vitro
- PMID: 15687192
- PMCID: PMC545626
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.4.1287-1292.2005
A polysaccharide deacetylase homologue, PdaA, in Bacillus subtilis acts as an N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase in vitro
Abstract
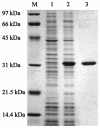
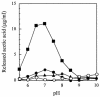
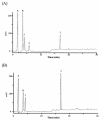
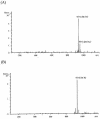
A polysaccharide deacetylase homologue, PdaA, was determined to act as an N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase in vitro. Histidine-tagged truncated PdaA (with the putative signal sequence removed) was overexpressed in Escherichia coli cells and purified. Measurement of deacetylase activity showed that PdaA could deacetylate peptidoglycan treated with N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase CwlH but could not deacetylate peptidoglycan treated with or without DL-endopeptidase LytF (CwlE). Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) and MS-MS analyses indicated that PdaA could deacetylate the N-acetylmuramic acid residues of purified glycan strands derived from Bacillus subtilis peptidoglycan.
Figures

References
-
- Blair, D. E., and D. M. van Aalten. 2004. Structures of Bacillus subtilis PdaA, a family 4 carbohydrate esterase, and a complex with N-acetyl-glucosamine. FEBS Lett. 570:13-19. - PubMed
-
- Fukushima, T., S. Ishikawa, H. Yamamoto, N. Ogasawara, and J. Sekiguchi. 2003. Transcriptional, functional and cytochemical analyses of the veg gene in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biochem. 133:475-483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

