PDZ interaction site in ephrinB2 is required for the remodeling of lymphatic vasculature
- PMID: 15687262
- PMCID: PMC546518
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.330105
PDZ interaction site in ephrinB2 is required for the remodeling of lymphatic vasculature
Erratum in
- Genes Dev. 2006 Jul 1;20(13):1829
Abstract
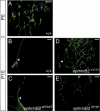
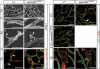
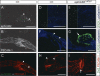
The transmembrane ligand ephrinB2 and its cognate Eph receptor tyrosine kinases are important regulators of embryonic blood vascular morphogenesis. However, the molecular mechanisms required for ephrinB2 transduced cellular signaling in vivo have not been characterized. To address this question, we generated two sets of knock-in mice: ephrinB2DeltaV mice expressed ephrinB2 lacking the C-terminal PDZ interaction site, and ephrinB2(5F) mice expressed ephrinB2 in which the five conserved tyrosine residues were replaced by phenylalanine to disrupt phosphotyrosine-dependent signaling events. Our analysis revealed that the homozygous mutant mice survived the requirement of ephrinB2 in embryonic blood vascular remodeling. However, ephrinB2DeltaV/DeltaV mice exhibited major lymphatic defects, including a failure to remodel their primary lymphatic capillary plexus into a hierarchical vessel network, hyperplasia, and lack of luminal valve formation. Unexpectedly, ephrinB2(5F/5F) mice displayed only a mild lymphatic phenotype. Our studies define ephrinB2 as an essential regulator of lymphatic development and indicate that interactions with PDZ domain effectors are required to mediate its functions.
Figures
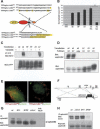
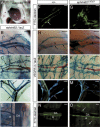
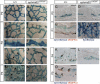
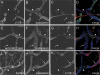
References
-
- Adams R.H. 2002. Vascular patterning by Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and ephrins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 13: 55-60. - PubMed
-
- Adams R.H., Wilkinson, G.A., Weiss, C., Diella, F., Gale, N.W., Deutsch, U., Risau, W., and Klein, R. 1999. Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: De-marcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes & Dev. 13: 295-306. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams R.H., Diella, F., Hennig, S., Helmbacher, F., Deutsch, U., and Klein, R. 2001. The cytoplasmic domain of the ligand ephrinB2 is required for vascular morphogenesis but not cranial neural crest migration. Cell 104: 57-69. - PubMed
-
- Alitalo K. and Carmeliet, P. 2002. Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell 1: 219-227. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla R., Bruckner, K., Orioli, D., Bergemann, A.D., Flanagan, J.G., and Klein, R. 1996. Similarities and differences in the way transmembrane-type ligands interact with the Elk subclass of Eph receptors. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 8: 199-209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
