Structural features of the focal adhesion kinase-paxillin complex give insight into the dynamics of focal adhesion assembly
- PMID: 15689512
- PMCID: PMC2279287
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.041107205
Structural features of the focal adhesion kinase-paxillin complex give insight into the dynamics of focal adhesion assembly
Abstract
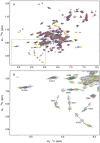
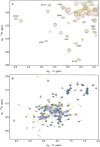
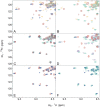
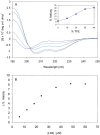
The C-terminal region of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) consists of a right-turn, elongated, four-helix bundle termed the focal adhesion targeting (FAT) domain. The structure of this domain is maintained by hydrophobic interactions, and this domain is also the proposed binding site for the focal adhesion protein paxillin. Paxillin contains five well-conserved LD motifs, which have been implicated in the binding of many focal adhesion proteins. In this study we determined that LD4 binds specifically to only a single site between the H2 and H3 helices of the FAT domain and that the C-terminal end of LD4 is oriented toward the H2-H3 loop. Comparisons of chemical-shift perturbations in NMR spectra of the FAT domain in complex with the binding region of paxillin and the FAT domain bound to both the LD2 and LD4 motifs allowed us to construct a model of FAK-paxillin binding and suggest a possible mechanism of focal adhesion disassembly.
Figures



References
-
- Arold, S.T., Hoellerer, M.K., and Noble, M.E. 2002. The structural basis of localization and signaling by the focal adhesion targeting domain. Structure 10 319–327. - PubMed
-
- Bertini, I., Donaire, A., Luchinat, C., and Rosato, A. 1997. Paramagnetic relaxation as a tool for solution structure determination: Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin as an example. Proteins 29 348–358. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M.C., Curtis, M.S., and Turner, C.E. 1998. Paxillin LD motifs may define a new family of protein recognition domains. Nat. Struct. Biol. 5 677–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

