GABAergic neurons in the central region of the spinal cord: a novel substrate for sympathetic inhibition
- PMID: 15689541
- PMCID: PMC6725977
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3740-04.2005
GABAergic neurons in the central region of the spinal cord: a novel substrate for sympathetic inhibition
Abstract
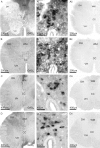
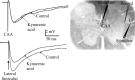
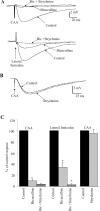
Homeostatic maintenance of widespread functions is critically dependent on the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. This activity is generated by the CNS acting on the sole output cells in the spinal cord, sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPNs). SPNs are subject to control from both supraspinal and spinal inputs that exert effects through activation of direct or indirect pathways. A high proportion of indirect control is attributable to activation of spinal interneurons in a number of locations. However, little is known about the different groups of interneurons with respect to their neurochemistry or function. In this study, we report on a novel group of GABAergic interneurons located in the spinal central autonomic area (CAA) that directly inhibit SPN activity. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated a group of neurons that contained mRNA for glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)65 and GAD67 within the CAA. Combining in situ hybridization with trans-synaptic labeling from the adrenal gland using pseudorabies virus identified presympathetic GABAergic neurons in the CAA. Electrical stimulation of the CAA elicited monosynaptic IPSPs in SPNs located laterally in the intermediolateral cell column. IPSPs were GABAergic, because they reversed at the chloride reversal potential and were blocked by bicuculline. Chemical activation of neurons in the CAA hyperpolarized SPNs, an effect that was also bicuculline sensitive. We conclude that the CAA contains GABAergic interneurons that impinge directly onto SPNs to inhibit their activity and suggest that these newly identified interneurons may play an essential role in the regulation of sympathetic activity and thus homeostasis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Stimulation within the rostral ventrolateral medulla can evoke monosynaptic GABAergic IPSPs in sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vitro.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Jan;77(1):229-35. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.1.229. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9120564
-
Tonic GABAergic inhibition of sympathetic preganglionic neurons: a novel substrate for sympathetic control.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 19;28(47):12445-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2951-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19020037 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic and glycinergic presympathetic neurons of rat medulla oblongata identified by retrograde transport of pseudorabies virus and in situ hybridization.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Nov 15;479(3):257-70. doi: 10.1002/cne.20332. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15457502
-
How sympathetic are your spinal cord circuits?Exp Physiol. 2015 Apr 1;100(4):365-71. doi: 10.1113/EP085031. Exp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25655449 Review.
-
GABA in the control of sympathetic preganglionic neurons.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002 May-Jun;29(5-6):507-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2002.03664.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12010200 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural circuitry in the regulation of adrenal corticosterone rhythmicity.Endocrine. 2005 Dec;28(3):325-32. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:28:3:325. Endocrine. 2005. PMID: 16388123 Review.
-
GABAergic Signaling during Spinal Cord Stimulation Reduces Cardiac Arrhythmias in a Porcine Model.Anesthesiology. 2023 Apr 1;138(4):372-387. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004516. Anesthesiology. 2023. PMID: 36724342 Free PMC article.
-
A New Population of Parvocellular Oxytocin Neurons Controlling Magnocellular Neuron Activity and Inflammatory Pain Processing.Neuron. 2016 Mar 16;89(6):1291-1304. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.041. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26948889 Free PMC article.
-
Central control of thermogenesis in mammals.Exp Physiol. 2008 Jul;93(7):773-97. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2007.041848. Epub 2008 May 9. Exp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18469069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis by neurons in the ventrolateral medulla and in the nucleus tractus solitarius.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):R277-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00039.2010. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20410479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson CR, McLachlan EM, Srb-Christie O (1989) Distribution of sympathetic preganglionic neurons and monoaminergic nerve terminals in the spinal cord of the rat. J Comp Neurol 283: 269-284. - PubMed
-
- Bacon SJ, Smith AD (1993) A monosynaptic pathway from an identified vasomotor centre in the medial prefrontal cortex to an autonomic area in the thoracic spinal cord. Neuroscience 54: 719-728. - PubMed
-
- Cabot JB (1990) Sympathetic preganglionic neurons: cytoarchitecture, ultrastructure, and biophysical properties. In: Central regulation of autonomic functions (Loewy AD, Spyer KM, eds), pp 22-34. New York: Oxford UP.
-
- Cabot JB, Alessi V, Carroll J, Ligorio M (1994) Spinal cord lamina V and lamina VII interneuronal projections to sympathetic preganglionic neurons. J Comp Neurol 347: 515-530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
