Beta-amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis involves c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent downregulation of Bcl-w
- PMID: 15689551
- PMCID: PMC6725978
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4736-04.2005
Beta-amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis involves c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent downregulation of Bcl-w
Abstract
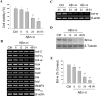
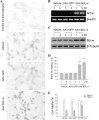
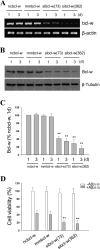
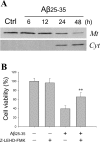
beta-Amyloid protein (Abeta) has been implicated as a key molecule in the neurodegenerative cascades of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Abeta directly induces neuronal apoptosis, suggesting an important role of Abeta neurotoxicity in AD neurodegeneration. However, the mechanism(s) of Abeta-induced neuronal apoptosis remain incompletely defined. In this study, we report that Abeta-induced neuronal death is preceded by selective alterations in expression of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis-related genes. Specifically, we observe that Abeta significantly reduces expression of antiapoptotic Bcl-w and Bcl-x(L), mildly affects expression of bim, Bcl-2, and bax, but does not alter expression of bak, bad, bik, bid, or BNIP3.Abeta-induced downregulation of Bcl-w appears to contribute to the mechanism of apoptosis, because Abeta-induced neuronal death was significantly increased by Bcl-w suppression but significantly reduced by Bcl-w overexpression. Downstream of Bcl-w, Abeta-induced neuronal apoptosis is characterized by mitochondrial release of second mitochondrion-derived activator of caspase (Smac), an important precursor event to cell death. We observed that Smac release was potentiated by suppression of Bcl-w and reduced by overexpression of Bcl-w. Next, we investigated the upstream mediator of Abeta-induced Bcl-w downregulation and Smac release. We observed that Abeta rapidly activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Pharmacological inhibition of JNK effectively inhibited all measures of Abeta apoptosis: Bcl-w downregulation, Smac release, and neuronal death. Together, these results suggest that the mechanism of Abeta-induced neuronal apoptosis sequentially involves JNK activation, Bcl-w downregulation, and release of mitochondrial Smac, followed by cell death. Complete elucidation of the mechanism of Abeta-induced apoptosis promises to accelerate development of neuroprotective interventions for the treatment of AD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estrogen regulates Bcl-w and Bim expression: role in protection against beta-amyloid peptide-induced neuronal death.J Neurosci. 2007 Feb 7;27(6):1422-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2382-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17287517 Free PMC article.
-
The c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway mediates Bax activation and subsequent neuronal apoptosis through interaction with Bim after transient focal cerebral ischemia.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 8;24(36):7879-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1745-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15356200 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-beta induces Smac release via AP-1/Bim activation in cerebral endothelial cells.J Neurosci. 2002 Nov 15;22(22):9764-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-22-09764.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12427831 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
Apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues.Apoptosis. 2023 Aug;28(7-8):943-957. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01848-y. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 37186274 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term social isolation stress exacerbates sex-specific neurodegeneration markers in a natural model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Sep 20;15:1250342. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1250342. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37810621 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein protects against Aβ25-35 induced apoptosis of PC12 cells through JNK signaling and modulation of Bcl-2 family messengers.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Jan 12;18(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0329-9. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28081713 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative and Anti-Apoptotic Roles of Silibinin in Reversing Learning and Memory Deficits in APP/PS1 Mice.Neurochem Res. 2017 Dec;42(12):3439-3445. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2389-3. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28852940
-
Cloning and characterization of the 5'UTR of the rat anti-apoptotic Bcl-w gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Nov 27;389(4):657-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.09.049. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19766102 Free PMC article.
-
Differential nigral expression of bcl-2 protein family in the pure and common forms of Dementia with Lewy bodies: relevance for dopaminergic neuronal vulnerability.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007;114(11):1469-77. doi: 10.1007/s00702-007-0765-x. Epub 2007 Jul 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007. PMID: 17641817
References
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, et al. (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 21: 383-421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonsson B, Martinou JC (2000) The Bcl-2 protein family. Exp Cell Res 256: 50-57. - PubMed
-
- Bae MA, Song BJ (2003) Critical role of c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase activation in troglitazone-induced apoptosis of human HepG2 hepatoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 63: 401-408. - PubMed
-
- Behl C, Davis JB, Klier FG, Schubert D (1994) Amyloid beta peptide induces necrosis rather than apoptosis. Brain Res 645: 253-264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
