Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis
- PMID: 15689635
- PMCID: PMC1138264
- DOI: 10.1155/JBB.2005.20
Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis
Abstract
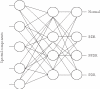
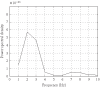
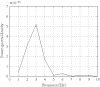
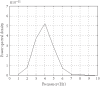
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the common complications of diabetes. Unfortunately, in many cases the patient is not aware of any symptoms until it is too late for effective treatment. Through analysis of evoked potential response of the retina, the optical nerve, and the optical brain center, a way will be paved for early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy and prognosis during the treatment process. In this paper, we present an artificial-neural-network-based method to classify diabetic retinopathy subjects according to changes in visual evoked potential spectral components and an anatomically realistic computer model of the human eye under normal and retinopathy conditions in a virtual environment using 3D Max Studio and Windows Movie Maker.
Figures











Similar articles
-
[Angiopathy and the eye].Vnitr Lek. 2010 Apr;56(4):333-9. Vnitr Lek. 2010. PMID: 20465107 Review. Czech.
-
[The visual evoked potentials in diabetic retinopathy].Oftalmologia. 2004;48(1):53-7. Oftalmologia. 2004. PMID: 15279420 Romanian.
-
Diabetic retinopathy. Screening and prevention of blindness. A doctoral thesis.Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 1997;(223):1-76. Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9559048
-
[Results of laser photocoagulation in patients with diabetic retinopathy developed as a complication of diabetes type 2].Klin Oczna. 2006;108(1-3):66-9. Klin Oczna. 2006. PMID: 16883944 Polish.
-
[Eye complications in diabetes. According to new criteria patients with diabetes should have ophthalmological examination at the time of diagnosis].Lakartidningen. 1998 Dec 2;95(49):5640-2. Lakartidningen. 1998. PMID: 9863304 Review. Swedish.
Cited by
-
Neural network-based diagnosing for optic nerve disease from visual-evoked potential.J Med Syst. 2007 Oct;31(5):391-6. doi: 10.1007/s10916-007-9081-0. J Med Syst. 2007. PMID: 17918693
-
Retinal Function in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes without Retinopathy: Insights from Pattern Electroretinogram and Pattern Visual Evoked Potentials Assessments.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 25;14(5):492. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14050492. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38472964 Free PMC article.
-
Visually evoked potentials after panretinal photocoagulation in omani patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2008 Apr;15(2):51-6. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.51992. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 21346837 Free PMC article.
-
Telehealth practice recommendations for diabetic retinopathy, second edition.Telemed J E Health. 2011 Dec;17(10):814-37. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2011.0075. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Telemed J E Health. 2011. PMID: 21970573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pattern Visual Evoked Potentials in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2012 Jul;7(3):225-30. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2012. PMID: 23264865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen M.S, Kao C.S, Fu C.C, Chen C.J, Tai T.Y. Incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy among non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects: a 4-year follow-up. Int J Epidemiol. 1995;24(4):787–795. - PubMed
-
- El-Asrar A.M, Al-Rubeaan K.A, Al-Amro S.A, Kangave D, Moharram O.A. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy among Saudi diabetics. Int Ophthalmol. 1998-1999;22(3):155–161. - PubMed
-
- Maberley D.A, King W, Cruess A.F, Koushik A. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in the Cree of James Bay. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2002;9(3):153–167. - PubMed
-
- Araki A, Ito H, Hattori A, et al. Risk factors for development of retinopathy in elderly Japanese patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(8):1184–1186. - PubMed
-
- Larsson L.I, Alm A, Bergenheim T, Lithner F, Bergstrom R. Retinopathy in diabetic patients aged 15–50 years in the county of Umea, Sweden. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1999;77(4):430–436. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

