The supramammillary nucleus mediates primary reinforcement via GABA(A) receptors
- PMID: 15689963
- PMCID: PMC1201464
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300660
The supramammillary nucleus mediates primary reinforcement via GABA(A) receptors
Abstract
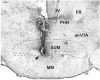
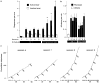
The supramammillary nucleus (SUM), a dorsal layer of the mammillary body, has recently been implicated in positive reinforcement. The present study examined whether GABA(A) receptors in the SUM or adjacent regions are involved in primary reinforcement using intracranial self-administration procedures. Rats learned quickly to lever-press for infusions of the GABA(A) antagonist picrotoxin into the SUM. Although picrotoxin was also self-administered into the posterior hypothalamic nuclei and anterior ventral tegmental area, these regions were less responsive to lower doses of picrotoxin than the SUM. The finding that rats learned to respond selectively on the lever triggering drug infusions is consistent with picrotoxin's reinforcing effect. Coadministration of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol disrupted picrotoxin self-administration, and another GABA(A) antagonist, bicuculline, was also self-administered into the SUM; thus, the reinforcing effect of picrotoxin is mediated by GABA(A) receptors. Since rats did not self-administer the GABA(B) antagonist 2-hydroxysaclofen into the SUM, the role of GABA(B) receptors may be distinct from that of GABA(A) receptors. Pretreatment with the dopamine receptor antagonist SCH 23390 (0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) extinguished picrotoxin self-administration into the SUM, suggesting that the reinforcing effects of GABA(A) receptor blockade depend on normal dopamine transmission. In conclusion, the blockade of GABA(A) receptors in the SUM is reinforcing, and the brain 'reward' circuitry appears to be tonically inhibited via supramammillary GABA(A) receptors and more extensive than the meso-limbic dopamine system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The midbrain raphe nuclei mediate primary reinforcement via GABA(A) receptors.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Feb;25(3):735-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05319.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17328772 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of the GABAA receptor antagonist picrotoxin into rat supramammillary nucleus induces c-Fos in reward-related brain structures. Supramammillary picrotoxin and c-Fos expression.BMC Neurosci. 2010 Aug 17;11:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-101. BMC Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20716371 Free PMC article.
-
GABA(A) receptor blockade in the anterior ventral tegmental area increases extracellular levels of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens of rats.J Neurochem. 1997 Jul;69(1):137-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69010137.x. J Neurochem. 1997. PMID: 9202304
-
Contribution of ventral tegmental GABA receptors to cocaine self-administration in rats.Neurochem Res. 2008 Mar;33(3):459-67. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9454-2. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 17943439 Free PMC article.
-
Possible substrates of ethanol reinforcement: GABA and dopamine.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Jun 28;654:61-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb25956.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992. PMID: 1321582 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Local circuit allowing hypothalamic control of hippocampal area CA2 activity and consequences for CA1.Elife. 2021 May 18;10:e63352. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63352. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34003113 Free PMC article.
-
Major diencephalic inputs to the hippocampus: supramammillary nucleus and nucleus reuniens. Circuitry and function.Prog Brain Res. 2015;219:121-44. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.03.008. Epub 2015 May 16. Prog Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26072237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary reinforcing effects of nicotine are triggered from multiple regions both inside and outside the ventral tegmental area.J Neurosci. 2006 Jan 18;26(3):723-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4542-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16421292 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 modulates the supramammillary nucleus-lateral hypothalamic neurocircuit to control ingestive and motivated behavior in a sex divergent manner.Mol Metab. 2019 Feb;20:178-193. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30528281 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin activity in the paraventricular and supramammillary nuclei of the hypothalamus is essential for social recognition memory in rats.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Feb;29(2):412-424. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02336-0. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38052983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvanitogiannis A, Flores C, Shizgal P. Fos-like immunoreactivity in the caudal diencephalon and brainstem following lateral hypothalamic self-stimulation. Behav Brain Res. 1997;88:275–279. - PubMed
-
- David V, Durkin TP, Cazala P. Self-administration of the GABAA antagonist bicuculline into the ventral tegmental area in mice: dependence on D2 dopaminergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology. 1997;130:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Ikemoto S, Murphy JM, McBride WJ. Self-infusion of GABAA antagonists directly into the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions. Behav Neurosci. 1997;111:369–380. - PubMed
-
- Ikemoto S, Sharpe LG. A head-attachable device for injecting nanoliter volumes of drug solutions into brain sites of freely moving rats. J Neurosci Methods. 2001;110:135–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

