Rab27a: a new face in beta cell metabolism-secretion coupling
- PMID: 15690078
- PMCID: PMC546431
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI24269
Rab27a: a new face in beta cell metabolism-secretion coupling
Abstract
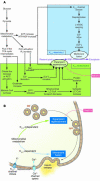
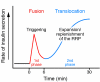
In pancreatic beta cells, not only insulin exocytosis per se, but translocation of beta granules toward the plasma membrane--an event upstream of exocytosis--are under the control of glucose. However, the molecular basis of this translocation has been poorly understood. Rab27a-mediated translocation of glucose-induced beta granules is reported in this issue of the JCI. Rab27a or its effector molecule may constitute a novel pharmacological target because potentiation of the Rab27a pathway is expected to restore beta cell glucose competency in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Comment on
-
Rab27a mediates the tight docking of insulin granules onto the plasma membrane during glucose stimulation.J Clin Invest. 2005 Feb;115(2):388-96. doi: 10.1172/JCI22955. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15690086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farfari S, Schulz V, Corkey B, Prentki M. Glucose-regulated anaplerosis and cataplerosis in pancreatic beta-cells: possible implication of a pyruvate/citrate shuttle in insulin secretion. Diabetes. 2000;49:718–726. - PubMed
-
- Zawalich WS, Zawalich KC. Regulation of insulin secretion by phospholipase C. Am. J. Physiol. 1996;271:E409–E416. - PubMed
-
- Nicholls LI, Ainscow EK, Rutter GA. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion does not require activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase: impact of adenovirus-mediated overexpression of PDH kinase and PDH phosphate phosphatase in pancreatic islets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;291:1081–1088. - PubMed

